
Polymorphism
n., plural: polymorphisms
[pɑliˈmɔɹfɪz(ə)m]
Definition: The occurrence of more than one kind or form. Three male Gouldian finches. Credit: GrifftheEcology.com.
Table of Contents
Polymorphism Definition
The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred to as polymorphism. What is meant by polymorphism in biology? In simplest terms, polymorphism is a process where two or more possibilities of a trait are found on one gene.
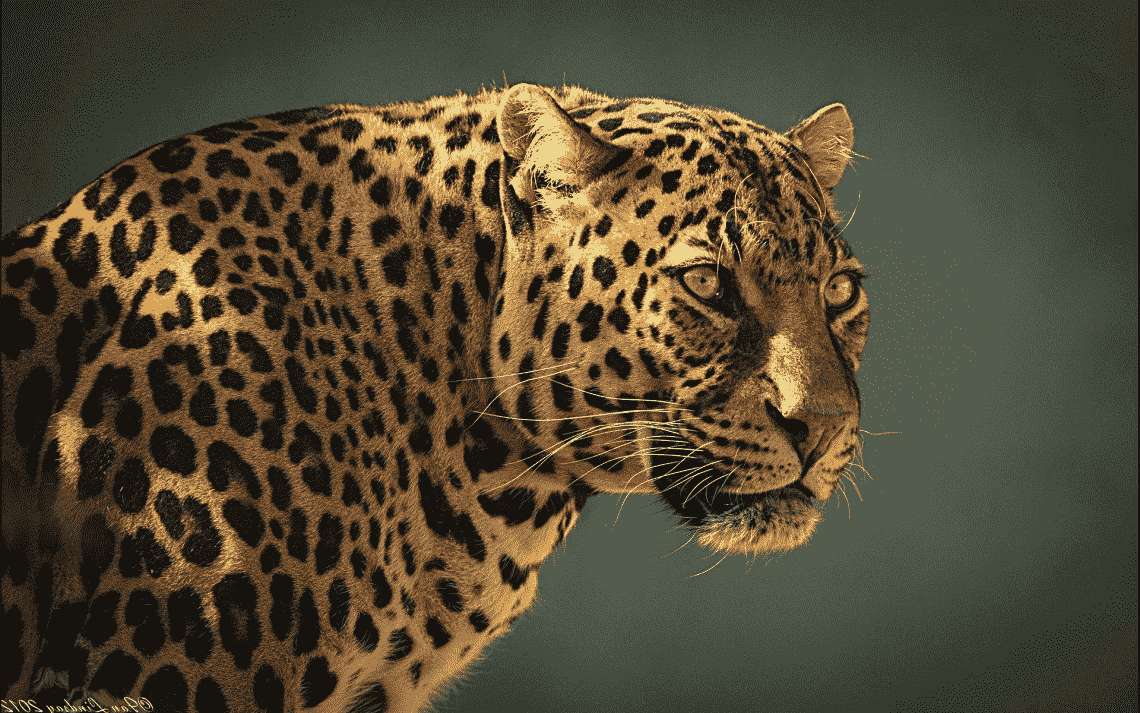
One example of polymorphism can be observed in jaguars. This species has more than one trait in its skin coloring. You must have seen jaguars with dark spots or light spots. This is because they have different morphs for their skin color. As there is more than one possible variation in their gene, this is called polymorphism.

Another example is the difference in pigmentation in the birds. Birds like Gouldian finch have striking color morphs due to variant alleles of pigmentation of non-melanic pigments. There are red and black color variants, and then further inter-morph difference exists because of the variants of these two alleles. Then there are differences in their feathers structure.

Introduction to terms “poly” and “morph”
Poly: By “poly”, we mean “multi” or “more than one”. Hence, genes having multiple traits, i.e. two or more than two traits, result in polymorphism.
Morph: This is a term that refers to various forms or stages in the life span of an organism. The different forms or stages can also be stated as “morphs.”
Polymorphic: The combined term refers to the existence of more than one form of traits in a species.
When we combine the two terms as polymorphism, it indicates the presence of a gene with multiple variations in polymorphic traits. If we take the above-given example of jaguars, if they have one polymorphic trait for that gene, it is called “monomorphic” because “mono” means “one”. It means if jaguars have only one skin color, then they are monomorphic.
Polymorphism is the occurrence of more than one kind or form of organisms of the same species that exist together in one locality. (biochemistry) Crystallization of a compound in at least two distinct forms. Etymology: Ancient Greek poly (many) + morph (form) + -ism. Compare: pleomorphism
Types of Polymorphism
Protein polymorphisms
Protein polymorphism occurs when more than one variation or allele occupies the locus of that particular gene within a population. Thus, this type of gene may lead to abnormal expressions from the nutrient protein, and this may then lead to many diseases.
RFLPs
In general, Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) is a new technique or method that makes use of variations in the homologous order of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid).
It helps differentiate singles or individuals, populations, or different species to pin the location and echolocation of the genes within a given order or in a sequence.
Copy Number Polymorphisms (CNPs)
This is another classification of polymorphism in humans. These are large duplications or deletions present in a few individuals in a population. Each person, on average, is different from another by eleven CNPs. One or more CNPs are present on the majority of chromosomes.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
SNPs are the most observed genetic variations among individuals. A nucleotide is a DNA building block. Each SNP stands for a single nucleotide variant. The replacement of the nucleotide, cytosine, with the nucleotide, thymine, is an example of single nucleotide polymorphism.
If a gene has more than one allele, it means SNP occurs in that gene. SNPs may also be responsible for variations in amino acid sequences. However, along with their association with a gene, single nucleotide polymorphisms may also occur in non-coding areas of DNA.
Around 90% of genetic variation in human beings is caused due to SNPs. It is observed that most of the variations do not affect cellular function in humans. However, some studies have shown that SNPs can be a reason for the development of various diseases such as cancer. They may also influence physiological responses to drugs.
DNA polymorphism
DNA sequences may vary significantly between different individuals. We collectively referred to these changes as DNA variants. Functional significance caused by most DNA variants is not very apparent. In such cases, these variations are called DNA polymorphisms. Polymorphism is a difference existing in the sequence of DNA that prevails in about 1% of the population.
The protein-coding genes occupy only 1% to 2% of the human genome. Therefore, a greater number of polymorphic variations will not have any direct impact on gene activity. However, if a polymorphic variation falls in the regulatory region of a gene, it can cause serious functional implications.
There are also those DNA variants that result in alterations in amino acids in the protein of DNA. But we still classify such variations as neutral, especially if the function of DNA protein is not affected by the change in amino acids.
DNA polymorphisms are useful for various purposes. For example, it is used in molecular medicine. DNA linkage analysis is a technique that helps to detect diseases through families. DNA polymorphism is also useful for Forensic DNA typing.
Enzyme and protein polymorphism
Enzymes are substances that show a great deal of polymorphism. A species’ population usually contains two or more enzyme variants. A single locus encodes them. They have slight variations in their amino acid sequence. These subtle variations usually cause them to migrate differently under electrophoresis.
A well-documented phenomenon in human populations is known as enzyme polymorphism. Electrophoretic studies have shown results indicating that around one-third of the enzymes in the human body experience genetic polymorphism.
Genetic polymorphism
The types mentioned above can all fall under genetic polymorphism. However, if we are particular with the term, it refers specifically, to the variation in genes. Genetic polymorphism is a type of polymorphism that involves multiple alleles that share the same genetic locus. Variants that have at least 1% occurrence frequency in that population is considered polymorphic.
Genetic polymorphs are able to exist because different genotypes within a population have proved to be fit and useful in various niches. As a result, the population retained them all. Thus, the variants of a particular trait became a part of that population.
Example: Cats and dogs have varying allele combinations for pigmentation. The locus E in dogs has five variants and their varying mixes result in different fur pigmentation patterns.
Misconceptions: there are two general misconceptions regarding polymorphism. They are as follows:
- Continuous variation traits
Traits such as height have continuous variations and they may as well be inherited but they do not come under the category of polymorphism.
- Geographical variants
Variants of a gene differing by geography are not included in polymorphism as the term is specific to variants existing in the same habitat at the same time.
Polymorphism vs. Mutation
A matter of confusion can arise between polymorphism and mutation since they both involve variation. However, the two are very different.
Mutation: defined as the variation in the genetic code. It could account for certain phenotypical or physical abnormalities. It can even be dangerous and even lethal. A mutation implies that there is a normal allele or variant of a gene that prevails in a population (wild-type). But on certain occasions, it got altered in some members of that species (less than 1%). It then led to the manifestation of traits different from the wild-type.
Examples:
Sickle cell anemia, where a single nucleotide change in the code results in the altered shape of red blood cells
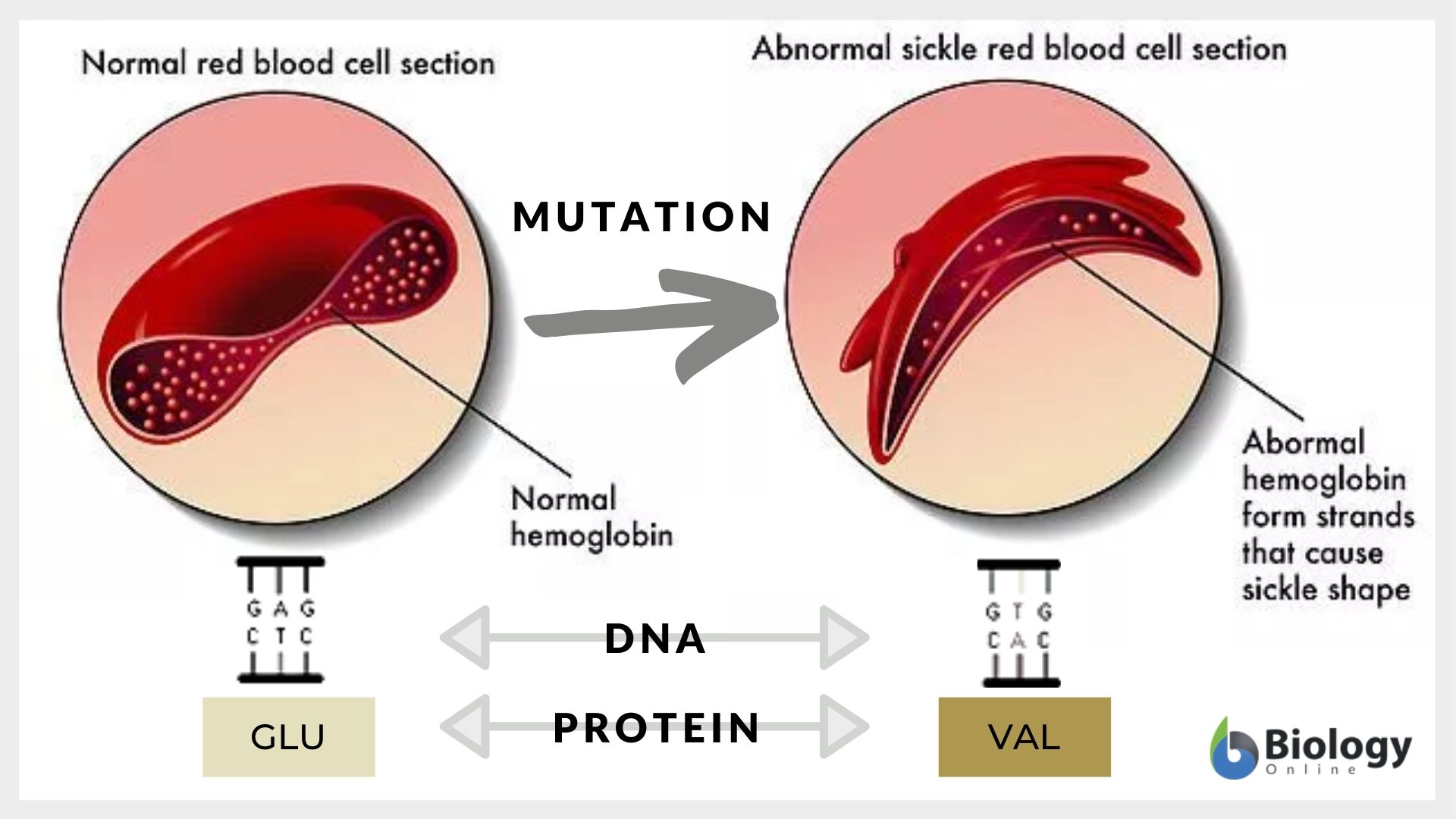
Cystic fibrosis – a mutation causes excess production of mucus that clogs the air passage in humans
Color blindness – mutated genes affect the ability of a person to see colors normally

Polymorphisms as variations that occur naturally in the genetic code as a result of species changing environment are typically beneficial for the species. Polymorphism implies that all alleles or variants of a gene are prevalent in the population (more than 1%), and all exhibit normal results.
About Evolutionary Theory of Polymorphism (Polymorphism Evolution)
The theory of evolution emphasizes that polymorphism results due to evolutionary processes. It is a hereditary trait, and the process of natural selection modifies it. According to the phenomenon regarding the history of evolution, it concludes that the process of evolutionary polymorphism is as simple as any feature of species. The evolutionary process indicates whether the stages and forms of organisms will be the exact copy or would they be distinguished through any means.
Involvement of DNA and maintaining balance
There is an involvement of one of two or more variants of a particular DNA sequence in polymorphism. It is observed that variation at a single base pair is the most common type of polymorphism. Long stretches of DNA can also be involved in polymorphism. This is called SNP.
- Polymorphism, in biology, is the genetic variation that is not in a continued state, or we can say that the discontinuous state concludes in the happening of a few various types of solo organisms among the members of its species.
- Polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more forms in the population of a species.
- A disconnected genetic dissimilarity can be divided among the individuals of a population into two or more than two sharply clear-cut forms.
- If we glance over another example, then the first instance is the human blood group and its types.
- In comparison, the individuals do not fall into sharp classes or groups but are almost imperceptibly ranked among the wide extremes.
Question: How is polymorphism different from inheritance?
Answer: Inheritance is essentially the passing-down of genes from parents to their offsprings. Polymorphism, on the other hand, is the inheritance of different forms or variants of the same gene.
If the frequency of two or more disconnected forms of a species is too high to be elaborated by mutation, the variation, even in the population displaying it, can also be polymorphic.
The usual function of polymorphism is to retain a variety of appearances or forms in the population of a species.
Examples of Polymorphism
What is an example of polymorphism in humans? Here are some examples of polymorphism to give you a better idea:
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the clearest example of polymorphism. It refers to the differences in size, height, shapes, voice, and other traits in male and female sexes of the same species, in addition to the difference in their sexual organs.

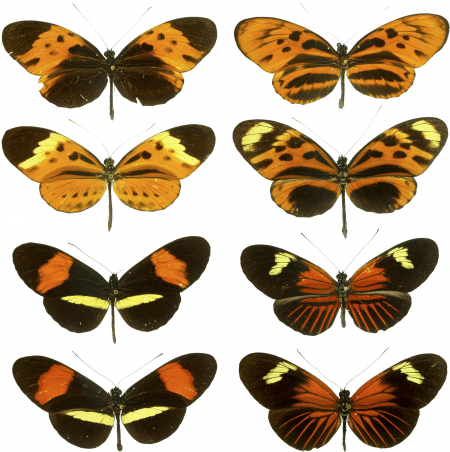
Mimetic Polymorphism in Butterflies
Another example of polymorphism is the mimetic form of butterflies. Apollo butterflies or Indian White admiral are the best examples to observe polymorphism. Butterflies make use of this phenomenon when trying to hide from their predators by mimicking the look of those species that are poisonous to their predators.

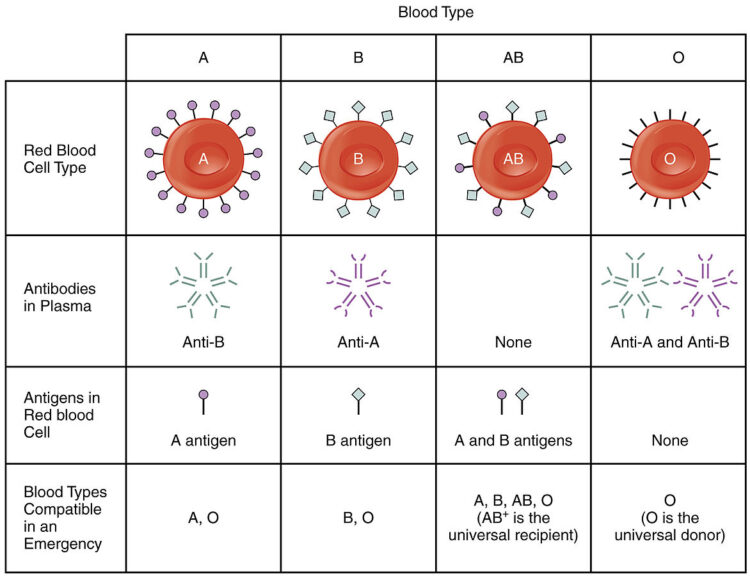
Blood Groups
All the types of blood groups are examples of genetic polymorphism, such as the ABO blood group system. We see this system having more than two morphs: A, B, AB, and O are the variants present in the entire human population, but these groups vary in proportion in different parts of the world. This trait is controlled by the presence of multiple alleles at one locus.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia has been observed in the tropical populations in Africa and India. It is an autosomal recessive disorder. (See Figure 4) It is responsible for causing anemia, a swollen spleen, joint pain, and some other frequent severe infections. It illustrates a balanced polymorphism. In sickle cell anemia, the heterozygous carrier becomes resistant to malaria.
Learn more about Sickle Cell Trait in this free Natural Selection – Examples tutorial.
Question: What are some examples of polymorphism in humans?
Answer: Blood groups, sickle cell anemia are some examples of polymorphism in humans.
What Causes Polymorphism?
There can be several causes of polymorphism. Some are listed below.
- One reason for maintaining polymorphism is to create a balance between variations that are created due to the process of mutation or due to natural selection.
- Frequency-dependent selection is also a cause of genetic variation or polymorphism.
- Heterozygous polymorphism works to maintain alleles.
- Migration of populations of species also results in polymorphism.
Zygosity can be explained as the degree of similarities or variations of alleles in an organism. The DNA sequence present in each gene is different for each individual. These differences or variations are called alleles.
A homozygous cell has a specific gene with identical alleles present on both of the homologous chromosomes. A homozygous-dominant individual has a specific trait that carries double copies of the dominant allele, e.g. AA. In contrast, a heterozygous cell is when it carries an allele pair (e.g. Aa) that does not code for the same phenotypic trait and one of them is dominant whereas the other is recessive.
What is heterozygote advantage? The heterozygote advantage means that the heterozygous genotype has a rather higher relative fitness than other possible genotypes. A single locus known as overdominance is responsible for the specific case of heterozygous advantage. For example, heterozygote for sickle cell anemia trait is observed to be more resistant to the debilitating effects of malaria than the homozygous dominant.
What is Transient Polymorphism?
When a rare gene starts gaining and preserving an over-all advantage, it will keep spreading and will reduce its normal allele as much as it reaches the status of a mutant. While this process is occurring, it generates a transient polymorphism. It happens because of intense environmental selective pressure. It causes the directional selection to eliminate one allele.
An example is a peppered moth. During the industrialization era of Britain, the soot from industries landed on the trees and turned them dark. During this time, the population of light-winged and dark-winged moths was equal, and their predators consumed them both. However, the population of white-winged moths began to decline as their light coloration made them an “easy prey” over the dark-winged moths. They are consumed more than the dark-winged moths. Eventually, the dark-winged moths became more predominant than the light-winged moths.

What is Balanced Polymorphism?
In balanced polymorphism, two different genes are maintained in a population of one species or organism. This happens because individuals that carry both versions of polymorphic genes are relatively fit or are more able to survive than those having two copies of either version alone. This evolutionary process that helps to maintain the two versions over a long time is referred to as balanced polymorphism or balancing selection.
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about polymorphism.
References
- Polymorphism. (2020). Genome.Gov. https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Polymorphism
- 18.7: Polymorphisms. (2016, August 2). Biology LibreTexts. https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_Biology_(Kimball)/18%3A_Evolution/18.07%3A_Polymorphisms
- Phillips, T. (2020, October 29). Genetic Polymorphism—Different Does Not Mean Mutated. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/genetic-polymorphism-what-is-it-375594
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2020). Polymorphism. Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/polymorphism-biology
- Kim, K.-W., Jackson, B. C., Zhang, H., Toews, D. P. L., Taylor, S. A., Greig, E. I., Lovette, I. J., Liu, M. M., Davison, A., Griffith, S. C., Zeng, K., & Burke, T. (2019). Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird. Nature Communications, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09806-6
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by BiologyOnline Editors.


