Search Results for: anti-g
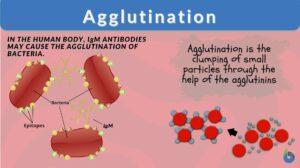
Agglutination
Agglutination Definition What does agglutination mean? It generally refers to the process of sticking together or the... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Glucocorticoid
Definition noun, plural: glucocorticoids Any of a group of corticosteroids involved in carbohydrate metabolism (e.g.... Read More
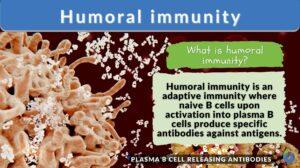
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
“Mutualism factor” could explain why body does not attack normal flora
When sadness reeks in and you feel as if you are all by yourself, think again. That is because you are never alone. As a... Read More
Corticosteroid
Definition noun, plural: corticosteroids A steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, e.g. glucocorticoids and... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Methampyrone
Methampyrone --> dipyrone (Science: chemical)... Read More
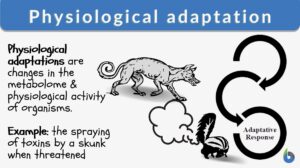
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
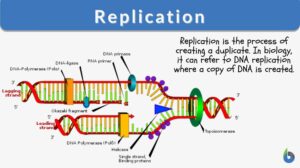
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
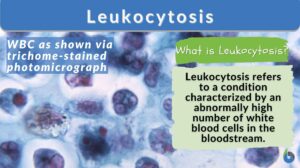
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
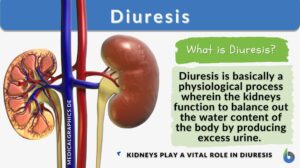
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Incomplete antibody
Incomplete antibody --> univalent antibody An incomplete form of antibody that may coat antigen, but which according to... Read More
Thanatosis – Faking Death To Escape Doom
Thanatosis -- pretending to be dead -- is one of the best strategies that certain wild animals came up with in order to... Read More
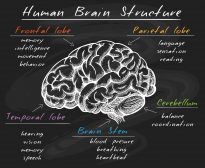
The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System
The Central Nervous System is arguably the most important part of the body because of the way it controls the biological... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
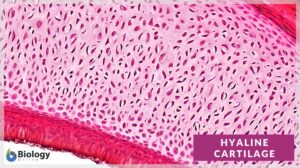
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Lactobacillus casei
Definition noun A non-pathogenic and harmless bacterium recognized widely as probiotics that controls growth of various... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
Glycosidase
Definition noun, plural: glycosidases (biochemistry) An enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of a... Read More
Protein pump
Protein pump - a kind of protein that is capable of pumping out compounds that could pose a threat to the cell. An example... Read More
Pentapeptide
Definition noun, plural: pentapeptides A peptide containing five amino acids Supplement Peptides are biomolecules that are... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Herpetology
Definition noun The branch of zoology that deals with reptiles and amphibians Supplement Herpetology is a sub-discipline of... Read More
Repolarization
Definition noun The process or act of repolarizing; the restoration of a polarized condition Supplement In physiology,... Read More