Search Results for: associated
Microtubule-associated protein
Definition noun, plural: microtubule-associated proteins Any of the proteins bound to the tubulin subunits of the... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
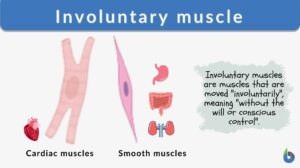
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
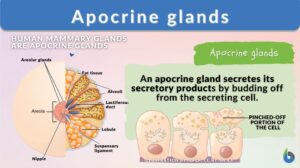
Apocrine gland
The human body is a complex assemblage of many different organs, systems, glands, bones, and tissues. Weighing any one over... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Companion cell
Definition noun (botany) Any of the metabolically-active parenchyma cells associated with a sieve tube element in the phloem... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Nuclear lamina
Definition noun plural: nuclear laminae or nuclear laminas nu·cle·ar lam·i·na, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈlæm.ɪ.nə (cell... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Osteoblast
Definition noun, plural: osteoblasts A type of bone cell that arises from fibroblasts, and upon maturity, becomes associated... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Y-linked gene
Definition noun, plural: Y-linked genes A gene located on the Y chromosome Supplement Y chromosome is the male chromosome of... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More