Search Results for: bases
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
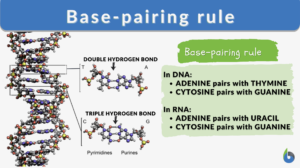
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
Continued from the previous tutorial that introduces protein synthesis... mRNA and tRNA mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Hydroxide ions
Hydroxide is a polyatomic ion consisting of oxygen and hydrogen: OH− It has a charge of −1. Hydroxide is one of the... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Definition noun A structural component of DNA that consists of 5-deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups involved in... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
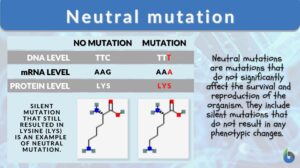
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Definition noun A DNA sequencing technique developed in 1976-1977 by Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbart to identify the sequence... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
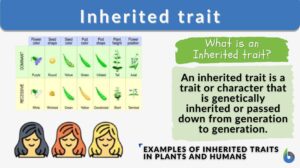
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Complementary DNA
Definition noun A double stranded DNA produced from the messenger RNA synthesis in a reaction catalyzed by an enzymes... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
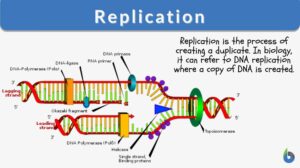
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Genetic code
Genetic code (Science: molecular biology) relationship between the sequence of bases in nucleic acid and the order of amino... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Modification enzyme
modification enzyme (Science: enzyme molecular biology) An enzyme that introduces minor bases into dNA or rNA or that alters... Read More
How cell fixes DNA damage
DNA repair strategies DNA is crucial to life. It carries the fundamental blueprint for the proper functioning of a cell.... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A single nucleotide (as... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More