Search Results for: chains
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
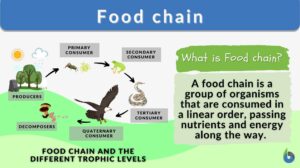
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
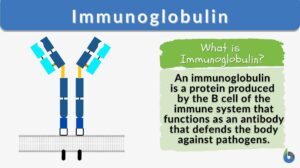
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
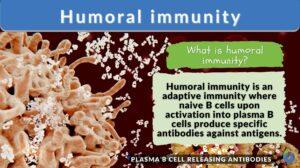
Humoral immunity
Let’s get to know where one should place humoral immunity, the topic of today’s discussion!! By the end of the article,... Read More
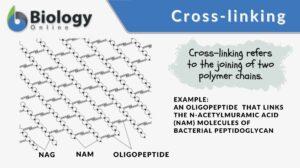
Cross-linking
Cross-linking Definition Cross-linking, in general, means the forming of cross-links between the joining structures. In... Read More
Mucopeptide
Definition noun A crystal lattice structure in the bacterial cell wall that is made up of linear chains of alternating amino... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
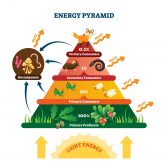
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
The previous tutorial on producers and consumers noted the reliance that organisms have on one another to obtain energy to... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
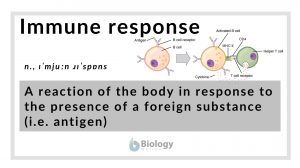
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Immunoglobulin A
Definition noun An immunoglobulin (antibody) that is characterized by its α-heavy chain, and its prevalence in mucous... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
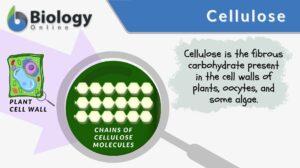
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Peptidoglycan
Definition noun, plural: peptidoglycans (1) A glycan (a polysaccharide) attached to short cross-linked oligopeptides in the... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
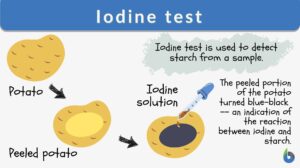
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Fibrinogen
Definition noun, plural: fibrinogens A soluble rod-shaped plasma glycoprotein (340 kd, 46 nm long) consisting of six peptide... Read More
Hydrocarbon chain
Definition noun, plural: hydrocarbon chains A chain consisting of only carbon and hydrogen atoms Supplement A hydrocarbon... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Cornification
Definition noun, plural: cornifications The process of forming a keratinized, horny layer of epidermis cornified,... Read More
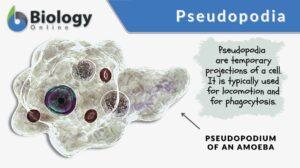
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More