Search Results for: charge
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
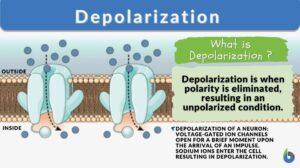
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
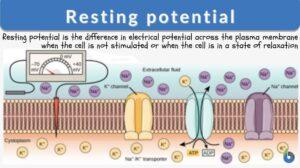
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Zwitterion
Definition noun, plural: zwitterions A molecule carrying both a positive and a negative charge Supplement A zwitterion is a... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Polarization
Definition noun (general) The condition of polarity (biology) The process or act of producing positive and negative... Read More
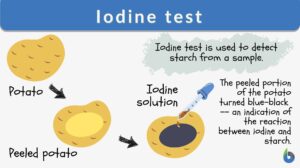
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
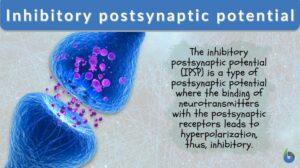
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
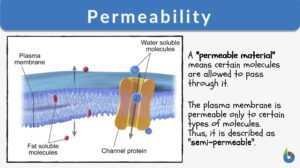
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
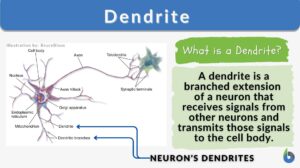
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis (Science: technique) separation of ionic molecules, (principally proteins) by the differential migration... Read More
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
Definition noun A type of postsynaptic potential where the binding of neurotransmitters with the postsynaptic receptors... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Polar molecule
Definition noun, plural: polar molecules A molecule with a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e. having... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
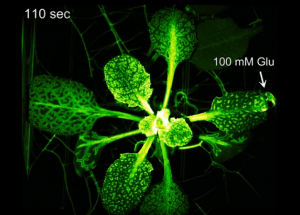
Plant sets off “SOS” for plant defense when it gets hurt
When herbivore, such as an insect, nibbles a plant leaf, the plant sets off an "SOS" or distress signal as one of the... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More