Search Results for: conversion
Gene conversion
Definition noun A nonreciprocal gene transfer in which an allele converts the other allele into the same form as its self,... Read More
Biochemical conversion process
Biochemical conversion process The use of living organisms or their products to convert organic material to... Read More
Lysogenic conversion
Lysogenic conversion --> lysogeny (Science: virology) The ability of some phages to survive in a bacterium as a result of... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
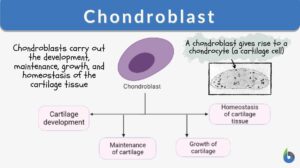
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Transformation
Definition noun, plural: transformations (1) The act, state or process of changing, such as in form or structure; the... Read More
Genomic imprinting
Definition noun A phenomenon in which the phenotype of the offspring depends on the source of the chromosome containing the... Read More
Extracellular inheritance
Definition noun A form of non-Mendelian inheritance in which a trait was transmitted from the parent to offspring through... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Trinucleotide repeat disorder
Definition noun, plural: trinucleotide repeat disorders Any of a set of genetic disorders caused by trinucleotide repeats... Read More
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
Enzyme activation
Enzyme activation conversion of an inactive form of an enzyme to one possessing metabolic activity. It includes 1)... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Infectious heredity
Definition noun A non-Mendelian inheritance in which an infectious particle within the cell of the host may bring changes in... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Non-Mendelian inheritance
Definition noun (genetics) A type of biological inheritance wherein the patterns of phenotypes do not accord with those as... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More