Search Results for: defects
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is a type of breeding or mating where closely related individuals with a common ancestor produce progenies with... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Quadrantanopia
Definition noun, plural: quadrantanopias A visual field defect characterized by a loss of vision in a quarter section of the... Read More
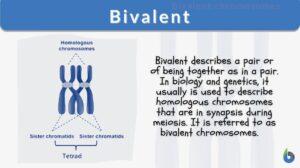
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Patau syndrome
Definition noun A genetic disorder caused by genetic changes in chromosome 13, such as an extra copy of chromosome 13... Read More
Embryology
Embryology Definition Embryology is a branch of biology that deals with the topics concerning gamete formation... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Rachischisis
Definition noun The embryological failure of the neural tube to fuse or close completely thereby resulting in the vertebrae... Read More
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
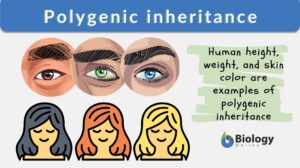
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Teratogenesis
Definition noun The development of structural or functional malformations in an embryo or a fetus Supplement Abnormalities... Read More
Austin disease
Definition noun A type of lysosomal storage disease that is often caused by a deficiency in multiple sulfatase enzymes, or... Read More
Mucolipidosis
Definition noun A type of mucopolysaccharides and mucolipids Supplement Lysosomal storage disease is a collective term for... Read More
Examples of Natural Selection
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Darwin's Finches Darwin's finches are an excellent example of the way in... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
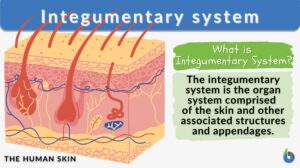
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Consanguinity
Definition noun, plural: consanguinities A relationship that arises from having a common ancestor;... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More