Search Results for: degraded
Carbohydrate
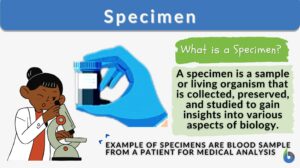
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Ribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: ribonucleotides ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌraɪbəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A form of nucleotide in... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Guanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of guanine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
Depolymerization
Definition noun, plural: depolymerizations The act of process of breaking down a polymer into smaller units or... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Protoplasm
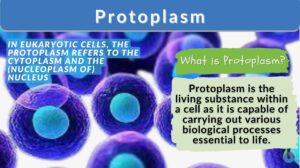
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Peroxisome
Definition noun, plural: peroxiomes A cell organelle whose major function is for the breakdown of very long chain of fatty... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More
Axon terminal
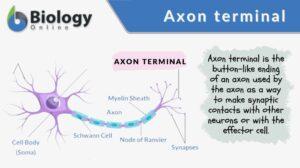
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Microsphere
A spherical shell that is usually made of a biodegradable or resorbable plastic polymer, that has a very small diameter... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More