Search Results for: discovery
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Scientists discover the gene that causes the smell of the earth and leads camels to water
Scientists at the John Innes Centre (JIC), Norwich(1) have discovered the gene that gives freshly turned soil its... Read More
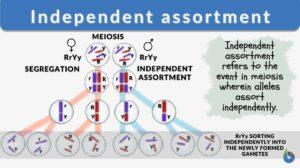
Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment Definition Independent assortment refers to the alleles or genes that sort into the newly formed... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
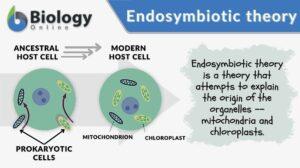
Endosymbiotic theory
A eukaryotic cell is distinct from a prokaryotic cell by the presence of membrane-bound cellular structures called... Read More
Chloroplast
Chloroplast Definition What is chloroplast? In biology, a chloroplast refers to the organelle found within the cell of... Read More
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity
At Home in the Universe: The Search for the Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity ... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
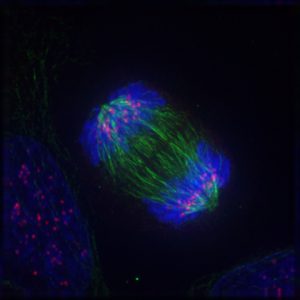
Cells know when to separate at mitosis
How do cells know when to separate during mitosis? A molecule called BubR1 was found to regulate the timing of the division... Read More
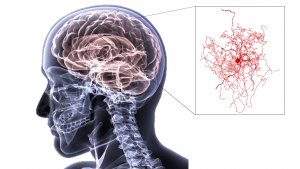
Newly identified human brain neuron may have unique genetic signature
Dubbed as "rosehip neuron", a new brain neuron recently discovered is unique based on its morphology and the set of genes it... Read More
Genetic Engineering Advantages & Disadvantages
Through genetic engineering, scientists are able to move desirable genes from one plant or animal to another or... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
photomedicine
Photomedicine Definition Photomedicine is a branch of medicine that specializes in the therapeutic application of light. As... Read More
Microbiology
Definition noun The branch of science that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living... Read More
A New Theory on the Origin of Animal Multicellularity
Multicellular life, purportedly, started around 600 million years ago. From single-celled, certain organisms eventually... Read More
Sex Reversal – When Males Grew Ovaries Instead of Testes
Summary: Sex reversal is not unusual in some animals, especially in invertebrates. As for the vertebrates, there are... Read More
SELFISH GENE – selfish to persist
What is a selfish gene? A selfish gene is not a gene that makes an individual selfish. In fact, it may even be involved in... Read More
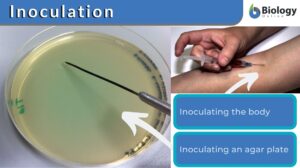
Inoculation
Inoculation Definition In Immunology, inoculation is defined as the process of introducing an antigenic substance or... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Geographical History
Written by: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Peer-reviewed by: Cathy Buntting, Ph.D. and Andrea Soanes New Zealand is... Read More
Pharmacology
Definition noun The branch in medicine that deals with the study of drugs, especially their action, use, preparation, and... Read More