Search Results for: double
Double-voided specimen
Double-voided specimen this refers to a urine specimen which is collected after first emptying the bladder and then waiting... Read More
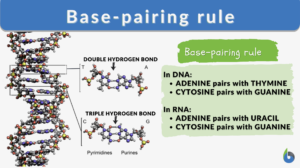
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Double stranded DNA virus
Definition noun Any of the viruses belonging to the Class I of Baltimore classification system characterized by having a... Read More
Double bond
Double bond (Science: chemistry) a covalent bond resulting from the sharing of two pairs of electrons; e.g., H2C==CH2... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
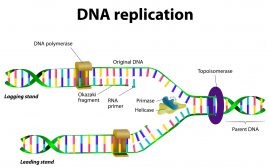
DNA Structure & DNA Replication
Previous pages in this tutorial have described the basics of a cell, the energy required by these cells and how energy is... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: polyunsaturated fatty acids Any of a group of unsaturated fatty acids characterized by having more... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
Cis fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: cis fatty acids A fatty acid in a cis configuration, i.e. two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Monounsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: monounsaturated fatty acids Any of a group of unsaturated fatty acids characterized by having a... Read More
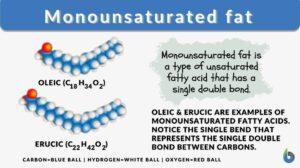
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Prostaglandin
Definition noun, plural: prostaglandins A group of eicosanoids, structurally characterized as 20-carbon unsaturated fatty... Read More
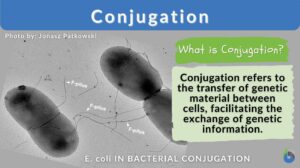
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Micrometer
micrometer An instrument, used with a telescope or microscope, for measuring minute distances, or the apparent diameters of... Read More
Hydrocarbon
Definition noun, plural: hydrocarbons An organic molecule comprised exclusively of carbon and hydrogen atoms Supplement A... Read More
SsRNA-RT virus
Definition noun, plural: ssRNA-RT viruses Single-stranded RNA virus with a positive sense, single stranded RNA genome but... Read More
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Definition noun A structural component of DNA that consists of 5-deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups involved in... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Unsaturated fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: unsaturated fatty acids The unsaturated fatty acid is a form of fatty acid containing one or more... Read More
Omega-6 fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: omega-6 fatty acids A type of polyunsaturated fatty acid in which the first double bond is between... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Double circulation
Definition noun A type of blood circulation system in which the blood flows through the heart twice. In this type of... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More