Search Results for: electricity
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Conduction
Conduction (Science: physics, physiology) The transfer of sound waves, heat, nervous impulses or electricity. Origin: L.... Read More
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More
Theory of Neuroscience
Nezih OKTAR Journal of Neurological Sciences (Turkish) 2006, Volume 23, Number 3, Page(s) 155-158. An Open Access... Read More
Waste management
Waste management refers to the various schemes to manage and dispose of wastes. It can be by discarding, destroying,... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Electronegative
Electronegative (Science: chemistry, physics) Relating to or charged with negative electricity. Normally refers to an... Read More
Physicology
physicology --> physics The science of nature, or of natural objects; that branch of science which treats of the laws and... Read More
Insulation
Insulation 1. The act of insulating, or the state of being insulated; detachment from other objects; isolation. 2. (Science:... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Stimulation
Stimulation 1. The act of stimulating, or the state of being stimulated. 2. (Science: physiology) The irritating action of... Read More
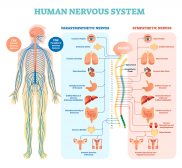
The Human Nervous System
The nervous system is essentially a biological information highway, and is responsible for controlling all the biological... Read More