Search Results for: enzymatic
Enzymatic synthesis
Enzymatic synthesis synthesis by enzymes. See:... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
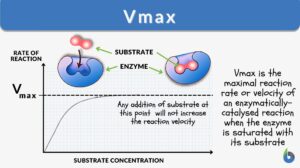
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Definition noun A catalytic decomposition of a chemical compound by reaction with water, such as the conversion of... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition noun plural: adenosine triphosphates (biochemistry) An organic compound that is... Read More
Respiration
Definition noun, plural: respirations Any of the various analogous processes by which there is an exchange of... Read More
Citric Acid Cycle
Definition noun (1) A cycle of reactions catalyzed by enzymes in which pyruvate derived from nutrients and converted to... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Testosterone
Definition noun, plural: testosterones A steroid hormone with a chemical formula of C19H28O2, and is regarded as the primary... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Phosphorescence
Definition noun The delayed emission of light at temperatures below incandescence, as a result of a previous light... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
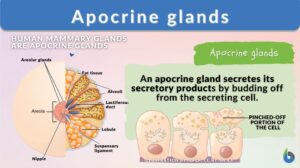
Apocrine gland
The human body is a complex assemblage of many different organs, systems, glands, bones, and tissues. Weighing any one over... Read More
DNA polymerase I
Definition noun The first known DNA polymerase, encoded by polA gene, and is involved in DNA replication in... Read More
Pancreatic juice
Definition noun The transparent fluid secreted by the pancreas composed mainly of water, electrolytes, and... Read More
Proteinoplast
Definition noun, plural: proteinoplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores and modifies protein Supplement Plastids are... Read More
Pioneer species
You might have come across news of some barren lands turning into luscious grasslands or forests after decades? Or you might... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Oxidative phosphorylation
Definition noun A metabolic pathway that generates ATP from ADP through phosphorylation that derives the energy from the... Read More