Search Results for: epinephrine
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Hormone Production
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system.... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
White adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: white adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals used to store energy and acts as... Read More
Beta-blocker
Definition noun, plural: beta-blockers A drug that blocks the action of endogenous catecholamines on beta-adrenergic... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
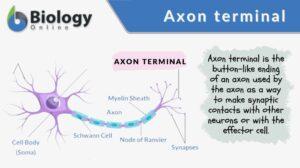
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Chromaffin cell
Definition noun, plural: chromaffin cells Any of the cells (mostly found) in adrenal medulla and in other ganglia of the... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
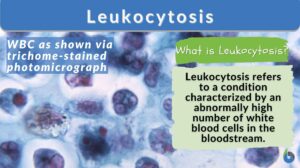
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Neurohormone
Definition noun, plural: neurohormones Any of the various hormones secreted by neuroendocrine cells Supplement A... Read More
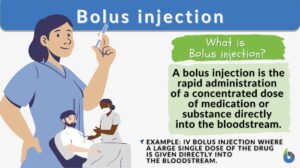
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Glycogenolysis
Definition noun The metabolic process of breaking down stored glycogen in liver into glucose subunits (i.e.... Read More