Search Results for: error
Technical error
technical error That component of experimental error that is due to the conduct of the experiment and in principle estimated... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Reliability coefficient
Definition noun (statistics) A quantitative expression of the reliability or consistency in the measurement of test scores,... Read More
Neurology of Illusions
As mentioned in the previous tutorial, Human Perception, illusions can be caused by mental disorders or misreading of the... Read More
Insight learning
Definition noun A type of learning that uses reason, especially to form conclusions, inferences, or judgments, to solve a... Read More
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology ... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
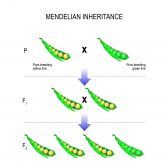
Inheritance and Probability
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is most famous in this field for his study... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
How cell fixes DNA damage
DNA repair strategies DNA is crucial to life. It carries the fundamental blueprint for the proper functioning of a cell.... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Selective Breeding
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, PhD Thousands of years before Darwin proposed evolution by natural selection and... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Erwin Chargaff
Quick Info (person) A biochemist known for his proposed Chargaff's rules that led to the discovery of the double helical... Read More
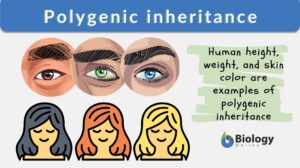
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Metabolic pathway
Definition noun A series of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes and are connected by their intermediates, i.e. the... Read More
Limitation
1. The act of limiting; the state or condition of being limited; as, the limitation of his authority was approved by the... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Hypermetropia
Hypermetropia --> hyperopia farsightedness or hyperopia occurs when a refractive error in which light rays entering the... Read More
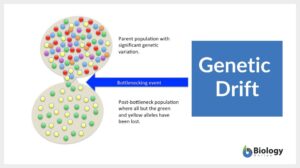
Genetic drift
Genetic Drift Definition What is genetic drift in simple terms? The simple definition of genetic drift ( also referred to... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Sos repair
SOS repair A system that repairs severely damaged bases in dNA by base excision and replacement, even if there is no... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More