Search Results for: excess
How High Sugar Level in Blood Damages the Blood Vessels
By Vicki Mozo Damage in the vasculature is common in individuals who have high sugar level in blood. It seems that an... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Definition noun High-density lipoprotein carrying a cholesterol molecule at its center Supplement A lipoprotein is an... Read More
Hypomelanism
All the body cells of living organisms bear some color due to one or the other pigment molecule or complex. The pigment can... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
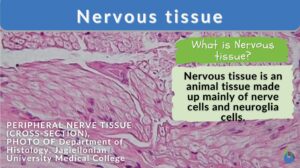
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Lipotropin
Definition noun, plural: lipotropins A polypeptide hormone of the anterior pituitary gland, presumably acts by promoting fat... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
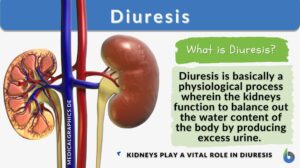
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Accessory Chromosome
Also known as B chromosomes, these chromosomes are excess chromosomes resulting from unsuccessful meiotic divisions where... Read More
Free radical
Free radical a chemically active atom or molecular fragment containing a chemical charge due to an excess or deficient... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Elephantiasis
Definition noun, plural: elephantiases A disease of the skin characterized by being thick, rough, hard, and fissured, like... Read More
Lacrimation
Definition noun, plural: lacrimations The shedding of tears; crying; tearing Supplement Lacrimation refers to the shedding... Read More
Enzyme inactivation
Enzyme inactivation The disappearance of an enzymes activity during in vitro conditions, such as during a lab preparation of... Read More
Alkaline reaction
Alkaline reaction Any test by which an alkaline reaction is recognised, such as the change of red litmus paper to blue, an... Read More
New Zealand’s Biodiversity
Written by: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Peer-reviewed by: Cathy Buntting, Ph.D. and Andrea Soanes Why is New... Read More