Search Results for: exercise
Anaerobic exercise
Definition noun A form of exercise involving highly intense activities that triggers anaerobic metabolism, especially when... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
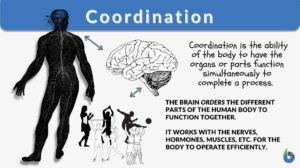
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies
Perspective Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies Cynthia M. Arbeeny Address... Read More
Lactate level
Definition noun A measure of the amount of lactic acid in the blood. Supplement The acid form of lactate (lactic acid) is... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Oxygen deficit
oxygen deficit The difference between oxygen uptake of the body during early stages of exercise and during a similar... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
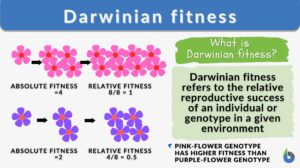
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
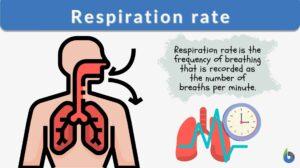
Respiration rate
Respiration Rate Definition Respiration rate is a vital life process that expresses the breathing rate in an organism... Read More
Limitation
1. The act of limiting; the state or condition of being limited; as, the limitation of his authority was approved by the... Read More
Physical fitness
Definition noun A general state of well-being and good health in which performance is optimal, i.e. effectively and... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
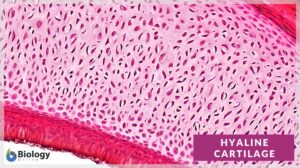
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Spontaneous
spontaneous 1. Proceding from natural feeling, temperament, or disposition, or from a native internal proneness, readiness,... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Glycogenolysis
Definition noun The metabolic process of breaking down stored glycogen in liver into glucose subunits (i.e.... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Adrenaline
A catecholamine secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress (trade name Adrenalin); stimulates autonomic nerve... Read More
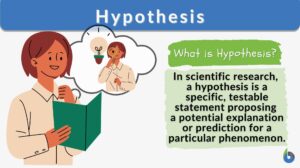
Hypothesis
What Is Hypothesis? A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method. It's a testable statement... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
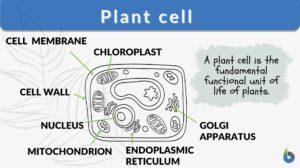
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
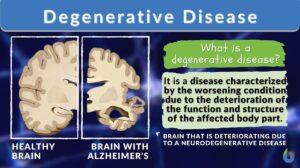
Degenerative disease
Degenerative Disease Definition A degenerative disease is defined as a disease characterized by the worsening condition due... Read More