Search Results for: folding
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Secondary structure
Definition noun A structure of a biological molecule characterized by the local folding within the biopolymer as a result... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Protein domain
Definition noun (1) An autonomously folding functional unit of a protein. (2) A part of protein that can fold, function... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
Disulfide bond
Definition noun (chemistry) (1) The single covalent bond formed from the coupling of thiol groups, especially of cysteine... Read More
Thermotropism
Definition noun, plural: photoropisms Movement or growth response of a cell or an organism to heat or changes in temperature... Read More
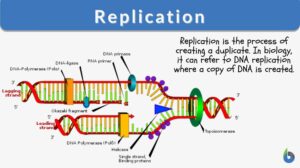
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
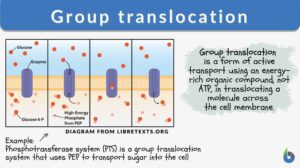
Group translocation
Group Translocation Definition Just like your “home” is a private place where you and your comfort are maintained due... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
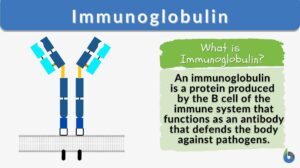
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More