Search Results for: fuel
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
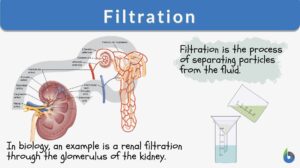
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Stoichiometric condition
stoichiometric condition That condition at which the proportion of the air-to-fuel is such that all combustible products... Read More
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Malic acid
Definition noun A dicarboxylic acid produced by a living organism, with a chemical formula: C4H6O5 Supplement Malic acid is... Read More
Non-sustainability
Non-Sustainability Definition Non-sustainability is the state in which human consumption or activities exceed the ability... Read More
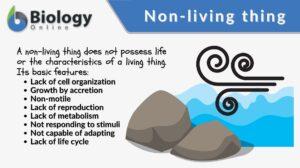
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Terrestrial plant
Definition noun, plural: terrestrial plants Any animal that lives, grows and reproduce in aquatic... Read More
Forest fire
Definition noun, plural: forest fires A wildfire that consumes a forest or a woodland Supplement A wildfire is a... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Human Biology – Food and Digestion
Food is what is required by humans to grow and survive, and provide a 'fuel' for the energy needed in our biological... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Biorefineries – Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions
Biorefineries - Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions ... Read More
Triglyceride
Definition noun, plural: triglycerides An energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules... Read More