Search Results for: glial
Pial-glial membrane
pial-glial membrane The dual outer lining of the brain and spinal cord, composed of the glial limiting membrane and the pia... Read More
Glial limiting membrane
Glial limiting membrane a dense, resilient membrane forming the true capsule of the brain and spinal cord, composed of the... Read More
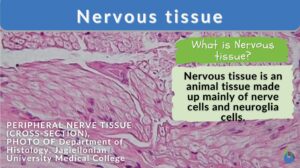
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūl A cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Central nervous system
Definition noun The part of the nervous system comprised of the brain, the brainstem, and the spinal cord Supplement In... Read More
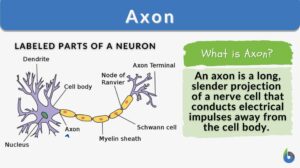
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
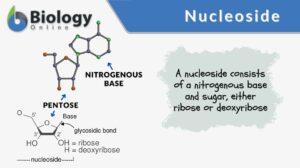
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Endogenous pyrogen
Definition noun, plural: endogenous pyrogens A type of pyrogen produced by activated immune cells, and incite the rise in... Read More
Herring body
Definition noun, plural: Herring bodies The neurosecretory terminal of the axons from the hypothalamus and located in the... Read More
Scientists brought dead pig brain partly back to life
Death is inevitable to any entity that has life. When there is a beginning there ought to be an end. However, the recent... Read More