Search Results for: hydrogen-1
Hydrogen bond
Definition noun plural: hydrogen bonds A type of chemical bond that is formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
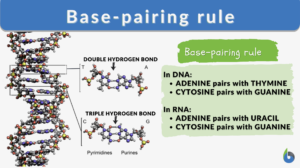
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Ionic bond
Definition noun plural: ionic bonds A type of chemical bond in which atoms, ions, or molecules are held together by... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Plant Cell Defense
Hydrogen Peroxide Plants release hydrogen peroxide in response to the presence of a fungal invasion, which attacks by... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Hydrocarbon chain
Definition noun, plural: hydrocarbon chains A chain consisting of only carbon and hydrogen atoms Supplement A hydrocarbon... Read More
Hydrocarbon
Definition noun, plural: hydrocarbons An organic molecule comprised exclusively of carbon and hydrogen atoms Supplement A... Read More
Chemiosmotic theory
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Hydrogen Acceptor
Any substance that is capable of becoming reduced and accepting hydrogen atoms, which allows the release of energy from such... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Chemical bond
Definition noun, plural: chemical bonds The attractive force that binds atoms, ions, or molecules in a chemical... Read More
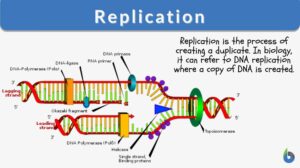
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More