Search Results for: ideal
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Environmental resistance
Environmental Resistance Definition Environmental resistance is such a process in which certain different elements or... Read More
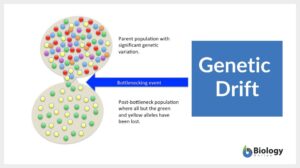
Genetic drift
Genetic Drift Definition What is genetic drift in simple terms? The simple definition of genetic drift ( also referred to... Read More
Dichotomous
Several English words are widely used across different fields of Science. One such term is dichotomous. We often use this... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
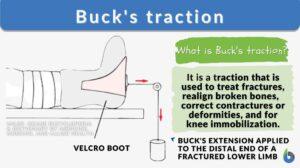
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
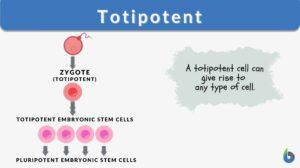
Totipotent
Totipotent Definition What is totipotent? In general terms, totipotency is defined as the ability of a single cell to... Read More
Realized niche
What is a niche? A niche can be defined as the means by which a species or an individual interacts with its environment. In... Read More
Genetic equilibrium
Definition noun A condition where a gene pool is not changing in frequency because the evolutionary forces acting upon the... Read More
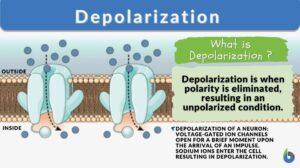
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Inbred strain
Definition noun, plural: inbred strains A strain of animal or plant that has undergone an inbreeding strategy (e.g. brother... Read More
Triplicate
Definition noun, plural: triplicates One of the three identical copies or replicates verb To make three copies... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
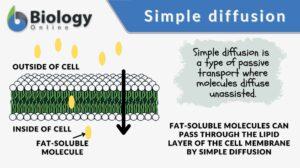
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Basic & Clinical Biostatistics (LANGE Basic Science)
Basic & Clinical Biostatistics (LANGE Basic Science) ... Read More
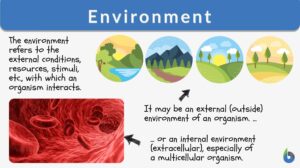
Environment
Environment Definition What does environment mean? If you mean physical environment, then it is defined as the surrounding... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Temperature
Temperature (Science: chemistry) temperature is proportional to the average random kinetic energy of ideal gases. The degree... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Cell differentiation
Cells are often described as the building blocks of life as they are the smallest unit used to build up organisms. Cells can... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Moisture content
Definition noun The weight of the water contained in an object or material, usually expressed as a percentage of... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More



















![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)
