Search Results for: industry
Biorefineries – Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions
Biorefineries - Industrial Processes and Products: Status Quo and Future Directions ... Read More
Biodiversity
The biological world or life on earth is a marvel that has amazed us since time immemorial. The rich natural diversity of... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Volatile oil
Volatile Oil Definition Volatile oils are aromatic compounds that are characterized by their volatility and inability to... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
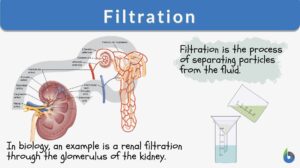
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies
Perspective Addressing the Unmet Medical Need for Safe and Effective Weight Loss Therapies Cynthia M. Arbeeny Address... Read More
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Tools and Methods for Data Collection in Ethnobotanical Studies of Homegardens
Tools and Methods for Data Collection in Ethnobotanical Studies of Homegardens CHRISTIAN R. VOGL BRIGITTE VOGL-LUKASSER... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Hydroxide ions
Hydroxide is a polyatomic ion consisting of oxygen and hydrogen: OH− It has a charge of −1. Hydroxide is one of the... Read More
Ultrafiltration
Definition noun (1) A high pressure filtration through a semipermeable membrane in which colloidal particles are retained... Read More
Abiotic Fixation
Definition noun It is part in nitrogen cycle wherein atmospheric nitrogen fixation carries out non-living components to... Read More
Bacillus megaterium
Definition noun An endospore forming rod-shaped bacterium recognized as an endophytes involved in the production of various... Read More
Cork cambium
Cork Cambium Definition Cork cambium is a secondary meristematic tissue that has a pivotal role in secondary growth in... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Flavin mononucleotide
Definition noun plural: flavin mononucleotides fla·vin mon·o·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌmɒnəʊˈnjuːklɪəˌtaɪd A... Read More
Diglyceride
Definition noun, plural: diglycerides A glyceride consisting of a glycerol and two fatty acid molecules joined through ester... Read More









![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)