Search Results for: insoluble
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
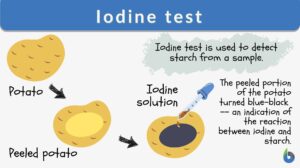
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Fibrinogen
Definition noun, plural: fibrinogens A soluble rod-shaped plasma glycoprotein (340 kd, 46 nm long) consisting of six peptide... Read More
Solubility
Definition noun (1) The quantity of a particular substance (solid, liquid, or gas solute) that can dissolve in a particular... Read More
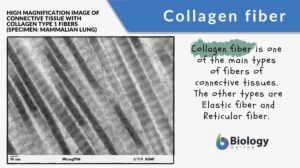
Collagen fiber
Definition of collagen fiber Collagen fiber is the fiber in the extracellular matrix of connective tissues characterized... Read More
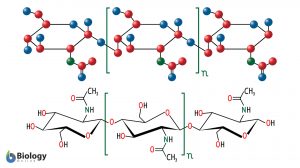
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Fat-soluble vitamin
Definition noun, plural: fat-soluble vitamins Any from the group of vitamins that are insoluble in water but soluble in fat... Read More
Fibronectin
Fibronectin (Science: protein) glycoprotein of high molecular weight (2 chains each of 250 kd linked by disulphide bonds)... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Xanthophyll
Definition noun, plural: xanthophylls A type of carotenoid in which its molecular structure contains... Read More
Metaprotein
metaprotein Nondescript term for a derived protein obtained by the action of acids or alkalis, soluble in weak acids or... Read More
Solubility test
solubility test A screening test for sickle cell haemoglobin (hb S), which is reduced by dithionite and is insoluble in... Read More
Carotenoid
Definition noun, plural: carotenoids (botany) Any of the pigment molecules, typically yellow, red, and orange, that interact... Read More
Protein Variety
The sequence of amino acids determines which type of protein it is. It is synthesized from a DNA strand, each DNA strand... Read More
Cytoplasmic matrix
Definition noun singular: cytoplasmic matrices cy·to·plas·mic ma·trix (1) Synonym for cell matrix, an insoluble,... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Scleroprotein
Definition noun, plural: scleroproteins A type of protein characterized by being fibrous and its function which is to... Read More
Phycobilin
Definition noun, plural: phycobilins A water-soluble accessory pigment found in red algae and... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
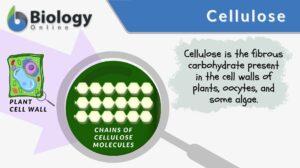
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Supernatant
supernatant (Science: chemistry) The soluble liquid fraction of a sample after centrifugation or precipitation of insoluble... Read More