Search Results for: insulin-like
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
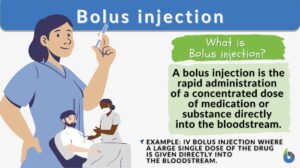
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
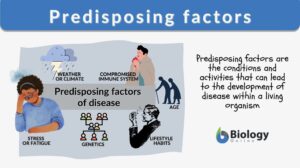
Predisposing factors
All organisms can be born with or develop a disease at any point in their lifetime. When someone is born with a disease, it... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Animal Growth Hormones
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. As mentioned in the previous tutorial, hormones are produced in... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Growth hormone
Definition noun, plural: growth hormones A polypeptide hormone that in humans and other animals essentially promotes... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
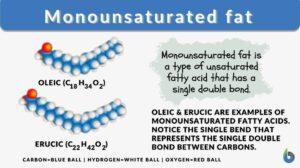
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More