Search Results for: interstitial
Interstitial fluid
Definition noun The fluid found in the intercellular spaces composed of water, amino acids, sugars, fatty acids,... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Extracellular fluid
Definition noun The body fluid outside the cell composed of blood plasma, interstitial fluid, lymph and transcellular... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Closed circulatory system
Definition noun A type of circulatory system where blood circulates within closed vessels, thus, blood is distinct from... Read More
Lymph capillary
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic capillaries (anatomy) A minute, thin-walled vessel of the lymphatic system that is... Read More
Luteinizing hormone
Definition noun, plural: luteinizing hormones A gonadotropin released by the gonadotropes of the anterior pituitary, and,... Read More
Open circulatory system
Definition noun A type of circulatory system wherein the hemolymph bathes the organs and tissues directly thus there is no... Read More
Transcellular fluid
Definition noun A bodily fluid found in chambers created by the linings of epithelial cells Supplement The extracellular... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Leydig cell
Leydig cell interstitial cells of the mammalian testis, involved in synthesis of testosterone. leydig cell Leydig cells,... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Aldosterone
Definition noun, plural: aldosterones A mineralocorticoid with a chemical formula of C21H28O5, and controls salt and water... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Pineal gland
Definition noun, plural: pineal glands A small endocrine gland shaped like a pinecone, located in the epithalamus, and... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Autoimmune disease
Definition noun, plural: autoimmune diseases A type of disease as a result of an immune response of the body against own... Read More
Pinealocyte
Definition noun, plural: pinealocytes The major cell type component of the pineal gland, and is involved in the production... Read More
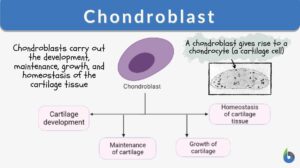
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Lipofuscin
Definition noun, plural: lipofuscins (cell biology) Any of the minute, yellow-brown, lipogenic pigment granules that... Read More
Circulatory fluid
Definition noun The fluid confined within the vessel in a closed circulatory system or that contained in a cavity (hemocoel)... Read More
Reticular fiber
Definition noun, plural: reticular fibers A type of connective tissue fiber that is made up of type III collagen secreted by... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
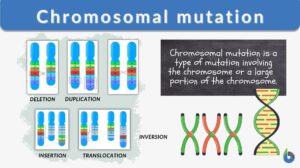
Chromosomal mutation
Every living thing is made up of DNA. Our DNA is what makes us unique and different in the world. Our DNA is made up of... Read More
Exudate cell
Definition noun, plural: exudate cells Any of the cells participating in the forming of exudate during inflammation or a... Read More
Extravascular fluid
Extravascular fluid All fluid outside the blood vessels, i.e., intracellular, interstitial, and transcellular fluid's; it... Read More
Blood vessel
Definition noun, plural: blood vessels Any of the vessels in cardiovascular system and functions by carrying blood... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Extracellular
Definition adjective Occurring or being (situated) outside the cell or cells. Supplement For example, extracellular fluid is... Read More
Lymphatic vessel
Definition noun, plural: lymphatic vessels (anatomy) A vessel that carries lymph and is responsible for the removal of... Read More
Amoebocyte
Amoebocyte (Science: organism) phagocytic cell found circulating in the body cavity of coelomates (particularly annelids and... Read More




![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)