Search Results for: involve
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Monogenic disease
Monogenic Disease Definition A monogenic disease is a diseased condition determined by the interaction of a single gene.... Read More
Covalent bond
Covalent Bond Definition What is a covalent bond? In chemistry and other fundamental science fields, a covalent bond is... Read More
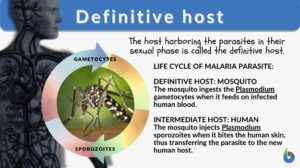
Definitive host
Different Biological Relationships The biological world is interconnected whether we notice it or not. All the life forms... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
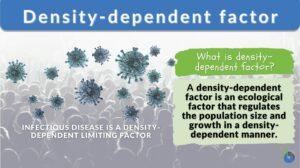
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
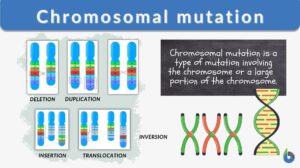
Chromosomal mutation
Every living thing is made up of DNA. Our DNA is what makes us unique and different in the world. Our DNA is made up of... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Duplication mutation
Definition noun A type of mutation in which a portion of a genetic material or a chromosome is duplicated or replicated,... Read More
Granulocytosis
Definition noun An increase in the number of circulating granulocytes in the bloodstream. Supplement Granulocytosis is a... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
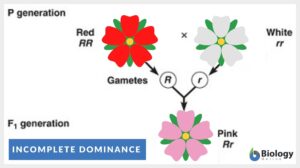
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
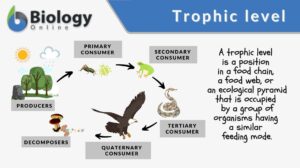
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
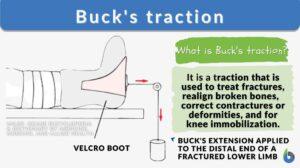
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Hydroxide ions
Hydroxide is a polyatomic ion consisting of oxygen and hydrogen: OH− It has a charge of −1. Hydroxide is one of the... Read More
Density dependent limiting factor
What Is A Density-Dependent Limiting Factor? Density-dependent limiting factors are limiting factors, which, depending on... Read More
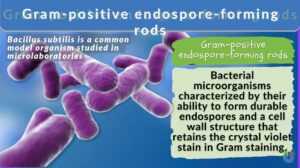
Gram-positive endospore-forming rods
Gram-Positive Endospore-Forming Rods Definition Gram-positive endospore-forming rods are a group of rod-shaped bacteria... Read More
Diachronic study
Diachronic study a study done over the course of time. For example, a longitudinal study of children with down syndrome... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Types of Transplants
Submitted to biologyonline.com on March 7, 2009 Published by biologyonline.com on March 29, 2009 Transplants are... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Hallucination – Are we the only ones “seeing” things or animals hallucinate, too?
Hallucination is defined as perceiving something that seems real but in fact, it is not. Some references take it as a... Read More
Abiotic and Biotic Factors
Abiotic factors are essentially non-living components that affect the living organisms of the freshwater community. When... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More






















![Hallucinations – a brain glitch – apparently could occur in animals, too. At least, according to a recent experiment on lab mice using optogenetics technique. [Img credit: Rick Harris (Flickr), by CC BY-SA 2.0]](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/hallucination-300x168.jpg)


