Search Results for: maintenance
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Biodiversity
The biological world or life on earth is a marvel that has amazed us since time immemorial. The rich natural diversity of... Read More
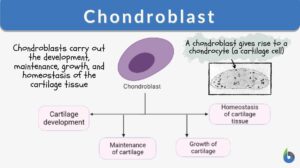
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Progestogen
Definition noun, plural: progestogens A steroid hormone that is activated by the binding to the progesterone receptor, and... Read More
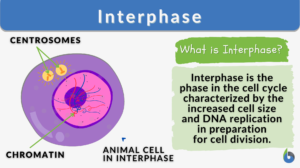
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
The Conscious & Unconscious Nervous System
The Central Nervous System is arguably the most important part of the body because of the way it controls the biological... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
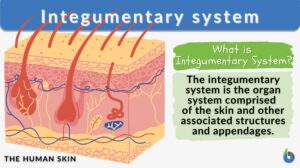
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Metabolic pathway
Definition noun A series of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes and are connected by their intermediates, i.e. the... Read More
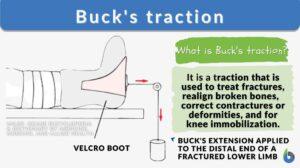
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Housekeeping gene
Definition noun, plural: housekeeping genes Any of the genes that are constitutively expressed at a relatively constant... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
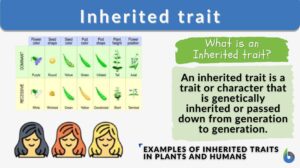
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
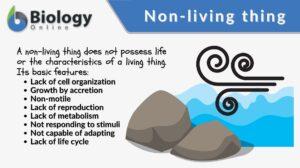
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More