Search Results for: messenger
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Second messenger
second messenger (Science: molecular biology) In many hormone sensitive systems the systemic hormone does not enter the... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
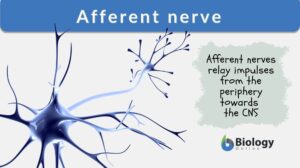
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Adenine nucleotide
Definition noun plural: adenine nucleotides A nucleotide wherein the nucleobase is adenine Details Overview A nucleotide... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Pentapeptide
Definition noun, plural: pentapeptides A peptide containing five amino acids Supplement Peptides are biomolecules that are... Read More
Spheroprotein
Definition noun, plural: spheroproteins A type of protein characterized by being globular or spherical in shape, and... Read More
Human Reproduction
Terminology and Concepts Primary reproductive organs are called gonads - testes in the male and ovaries in the female.... Read More
Human Perception – Neurology
A better understanding of human perception unlocks the key to how the mind works, an advantage when working with people with... Read More
Hormone Production
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in the endocrine system.... Read More
Ribosomal DNA
Definition noun DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA Supplement Ribosomal DNA is the sequence of DNA that codes for... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Protein Synthesis
If you have jumped straight to this page, you may wish to look at the previous tutorial about DNA, which gives background... Read More
Complementary DNA
Definition noun A double stranded DNA produced from the messenger RNA synthesis in a reaction catalyzed by an enzymes... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Modulation
modulation --> neuromodulation alteration in the effectiveness of voltage gated or ligand gated ion channels by changing... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Enhancer element
Enhancer element (Science: molecular biology) a dna sequence, present in the genomes of higher eukaryotes and of various... Read More