Search Results for: metabolize
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Methanogen
Definition noun, plural: methanogens An archaeabacterium capable of methanogenesis Supplement A methanogen pertains to any... Read More
Micrococcus luteus
Definition noun A gram-positive aerobic harmless bacterium involved in the conversion of nitrate to... Read More
Oxidation-fermentation test
Definition noun A test used to identify bacteria by the way they metabolize a carbohydrate substrate (e.g. glucose) whether... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Lycinibacillus fusiformis
Definition noun A long rod-shaped obligate aerobe organism that is able to utilize oxygen to metabolize numerous sugars... Read More
Methanotroph
Definition noun, plural: methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and... Read More
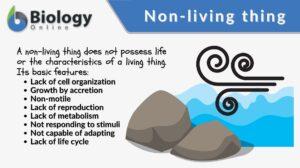
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Disruptive Selection
An evolutionary process known as disruptive selection (or disruptive natural selection) causes a population to become... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Alimentary glycosuria
Definition noun A form of glycosuria caused by the incapacity of the liver and other tissues to metabolize glucose faster... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
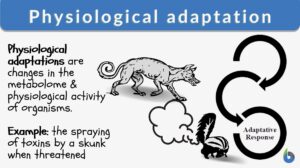
Physiological adaptation
If we look over evolutionary history, we find that it’s neither the most genius and intelligent nor the strongest and the... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Detritivore
Definition noun, plural: detritivores An organism that feeds on detritus or organic waste Supplement A detritivore pertains... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Effect of Chemicals on Growth & Development in Organisms
Plants Plants require a large number of elements to function properly, mainly carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen, essentially... Read More