Search Results for: molar
Molar extinction coefficient
Definition noun (spectrophotometry) The measure of how strongly a substance absorbs light at a particular wavelength, and is... Read More
Molar behaviour
molar behaviour (Science: psychology) behaviour described in large response units rather than smaller ones. Compare:... Read More
Beer-Lambert law
Definition noun The principal law in spectrometry in which it states that the absorbance at a given wavelength of light is... Read More
Dens serotinus
Dens serotinus --> third molar eighth permanent tooth in the maxilla and mandible on each side, making it the most... Read More
Third-order kinetics
third-order kinetics (Science: pharmacology) A term describing the reaction rate of a chemical reaction in which the rate... Read More
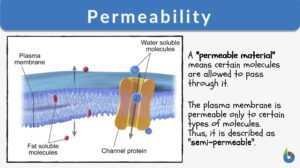
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Bicuspid tooth
Definition noun A tooth with two cusps; a premolar tooth. Supplement Bicuspid is located between the canine and molar teeth,... Read More
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Vant hoffs law
van't Hoff's law In stereochemistry, all optically active substances have one or more multivalent atoms united to four... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
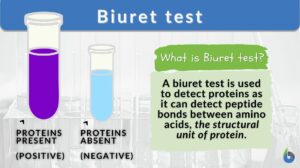
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
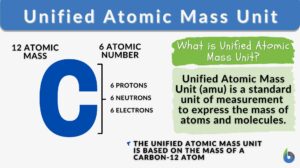
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
N-acetylglucosamine
Definition noun An amino sugar derivative of glucose, with a chemical formula of C8H15NO6, and serves as a major component... Read More
Tuber maxillae
tuber maxillae --> maxillary tuberosity The bulging lower extremity of the posterior surface of the body of the maxilla,... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Specific absorption coefficient
Definition noun A factor that measures the absorbance of light per unit of path length (of the spectrophotometer cuvette,... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More










![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)
