Search Results for: nerves
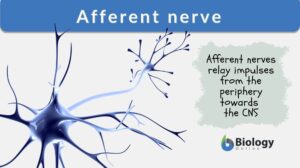
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Somatic nervous system
Definition noun The part of the peripheral nervous system that consists of afferent nerves responsible in relaying motor... Read More
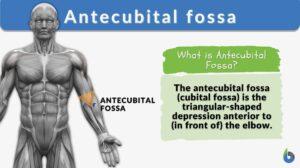
Antecubital fossa
Antecubital Fossa Definition The antecubital fossa or the cubital fossa is the triangular-shaped hollow depression between... Read More
Cranial nerve
Definition noun, plural: cranial nerves Any of the paired nerves emerging from the brain (including the brainstem but not... Read More
Coccygeal spinal nerve
Definition noun, plural: coccygeal spinal nerves Any of the pair of nerves that emerge from the coccygeal region of the... Read More
Efferent nerve
Definition noun, plural: efferent nerves The type of nerve that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system... Read More
Spinal nerve
Definition noun, plural: spinal nerves Any of the pairs of nerves emerging from the spinal cord, where each pair is attached... Read More
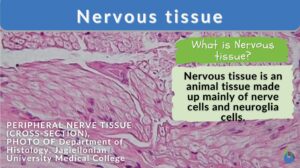
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
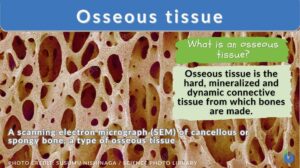
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
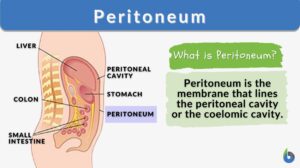
Peritoneum
What is the Peritoneum? The term peritoneum refers to the serous membrane that constitutes the biologically active inner... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Splanchnic
Definition adjective Of, pertaining to, relating to, near to, or describing the viscera or entrails;... Read More
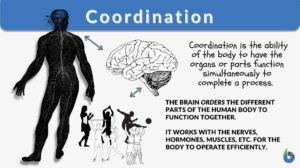
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Olfactory nerve
Definition noun, plural: olfactory nerves The cranial nerve comprised of sensory nerve fibers that carry impulses for the... Read More
Anterior primary division
Anterior primary division --> ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve (Science: anatomy, nerve) The larger,... Read More
Ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve
ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve (Science: anatomy, nerve) The larger, anterolaterally-directed major terminal branch... Read More
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
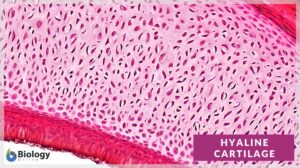
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
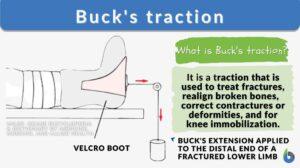
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
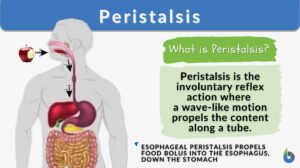
Peristalsis
What is Peristalsis? Peristalsis is the series of involuntary, wave-like muscle movements in the cylindrical, hollow tube... Read More
Internal auditory canal
Definition noun A short, narrow passageway through the temporal bone of the skull where the vestibular nerve and cochlear... Read More
Bell-Magendie law
Definition noun The principle referring to the separation of sensory and motor neurons of the spinal cord, where the... Read More
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (7th Ed) by F.H. Martini
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (7th Edition) ... Read More
Stimulation
Stimulation 1. The act of stimulating, or the state of being stimulated. 2. (Science: physiology) The irritating action of... Read More
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic guanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of guanosine monophosphate (chemical... Read More