Search Results for: parameters
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Microalgae
Microalgae Definition Microalgae (singular: microalga) are microscopic algal species as opposed to other algae that are... Read More
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is a theoretical framework that explains the historical shift in population dynamics as a... Read More
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetics Definition Phylogenetics is the scientific study of phylogeny. It studies evolutionary relationships among... Read More
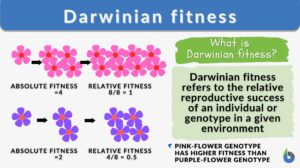
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and Behavior Having discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Neurology of Illusions
As mentioned in the previous tutorial, Human Perception, illusions can be caused by mental disorders or misreading of the... Read More







![Botany n., [ˈbɑt.ə.ni/] botany definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/botany-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)