Search Results for: pathological
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Skeletal system
What is the Skeletal System? How to define a skeleton? The skeletal system is the main framework that gives your body its... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
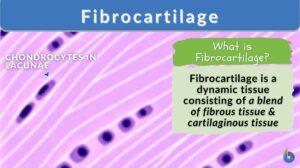
Fibrocartilage
What Is Fibrocartilage? Fibrocartilage is the strongest transitional connective tissue made up of collagen fibers and... Read More
Chronic disease
Chronic disease diseases which have one or more of the following characteristics: they are permanent, leave residual... Read More
Eicosanoid
Definition noun, plural: eicosanoids Any of the substances derived from arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty... Read More
Anhidrosis
Definition noun, plural: anhidroses A pathological condition characterized by the inability to sweat... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Metabolic disorder
Definition noun, plural: metabolic disorders A disorder in the metabolism, often caused by a dysfunctional enzyme as a... Read More
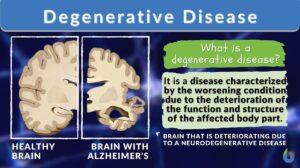
Degenerative disease
Degenerative Disease Definition A degenerative disease is defined as a disease characterized by the worsening condition due... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Glycogenosis
Definition noun, plural: glycogenoses A metabolic disorder caused by a defective glycogen metabolism resulting in the extra... Read More
Cholesterol
Definition noun A sterol or a modified steroid that is synthesized by animal cells to become an essential component of... Read More
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy Definition Hypertrophy refers to the enlargement or increase in the size of an organ or tissue due to the... Read More
Pathologic
Definition "adjective'' (1) Of, or pertaining pathology, especially on the structural and functional changes in tissues and... Read More
Epithelium
An epithelium is a type of animal tissue made up of densely packed cells (called epithelial cells) that rest on a basement... Read More
Respiration rate
Respiration Rate Definition Respiration rate is a vital life process that expresses the breathing rate in an organism... Read More
Heart sounds
Heart sounds The sounds heard over the cardiac region produced by the functioning of the heart. There are four distinct... Read More
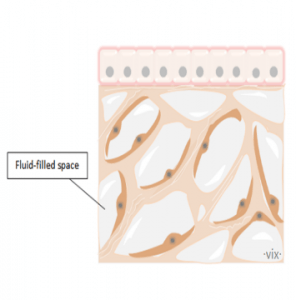
The interstitium – a new biological organ?
Scientists found, apparently by accident, a new biological organ and they want it called "interstitium". The discovery was... Read More