Search Results for: pertain
Spontaneous generation
Definition noun plural: spontaneous generations The previously popular notion that living organisms arise or develop from... Read More
Genetic variation
Definition noun, plural: genetic variations Variations of genomes between members of species, or between groups of species... Read More
Isotonicity
Definition noun The state of being isotonic, or having equal tension or tonicity Supplement In biology, tonicity pertains to... Read More
Homologous
Homologous Definition What is homologous? In general science, the word “homologous” is used to show a degree of... Read More
Zooplankton
Definition noun Animal or animal-like constituent of plankton, comprised mainly of freely floating protozoa, small... Read More
Neutrophile
Definition noun, plural: neutrophiles (1) A neutrophilic organism that lives and thrives in an environment with a... Read More
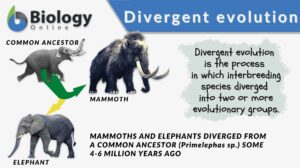
Divergent evolution
Divergent Evolution Definition Divergent evolution refers to the process by which interbreeding species diverged into two... Read More
Biocoenosis
Definition noun, plural: biocoenoses All the interacting organisms that live together in a specific habitat or biotope,... Read More
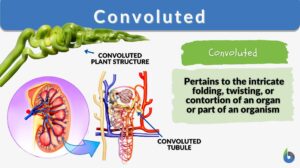
Convoluted
The word convoluted is often used to describe different things, especially structures or components, that have overlapped.... Read More
Apical bud
Apical Bud Definition The apical bud is the type of bud located at the top (apex) of the plant, particularly at the very... Read More
Ecological niche
Ecological Niche Definition An ecological niche refers to the interrelationship of a species with all the biotic and... Read More
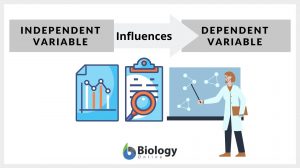
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Phytoplankton
Definition noun Photosynthetic (plant-like) constituent of plankton, mainly comprised of unicellular... Read More
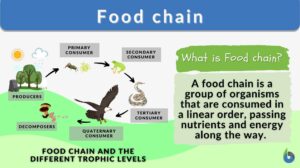
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
Erythroblast
Definition noun, plural: erythroblasts A nucleated red blood cell that develops into a reticulocyte Supplement The blood... Read More
Allotetraploid
Allotetraploid Definition An allotetraploid is an organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n). This is in contrast to the... Read More
Hypotonicity
Definition noun The state of being hypotonic, i.e. having lesser degree of tone or tension Supplement In biology, tonicity... Read More
Homeostatic equilibrium
Definition noun (1) The tendency of an organism or a cell to regulate its internal conditions, usually by a system of... Read More
Diurnal rhythm
Definition noun, plural: diurnal rhythms A biological rhythm that primarily express a periodicity during daylight... Read More
Biological clock
Definition noun, plural: biological clocks Any of the various mechanisms that regulate biological rhythms Supplement A... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Pseudogamy
Definition noun (1) A form of parthenogenesis wherein the sperm stimulates the egg cell to develop into an embryo without... Read More