Search Results for: phospholipids
Phospholipid
What is a phospholipid? Phospholipids are a subgroup of lipids. Other major types of lipids are fatty acids, sphingolipids,... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Phospholipid bilayer
Definition noun The two layers of phospholipids arranged in such a way that their hydrophobic tails are projecting inwards... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Chemical Composition of the Body
In order to fully understand the mechanisms of human physiology, it is important to have an understanding of the chemical... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Human Biology – Food and Digestion
Food is what is required by humans to grow and survive, and provide a 'fuel' for the energy needed in our biological... Read More
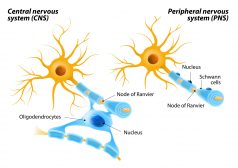
The Central Nervous System
Myelin Sheath Myelin is a substance that forms the myelin sheath associated with nerve cells. This sheath is a layer of... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Bacteriolysin
Definition noun, plural: bacteriolysins (1) A specific antibody that combines with bacterial cells (antigens) and, in the... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
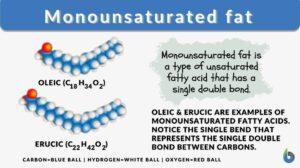
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Selective permeability
Definition noun A feature and a function of the plasma membrane that is essential to maintain homeostasis by regulating the... Read More
Hepatocyte
Definition noun, plural: hepatocytes Any of the large, polygonal-shaped cells in the liver. Supplement Hepatocytes are the... Read More
Diacylglycerol
Diacylglycerol glycerol substituted on the 1 and 2 hydroxyl groups with long chain fatty acyl residues. Dag is a normal... Read More
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis Definition Biosynthesis refers to the production (synthesis) of a complex chemical compound from simpler... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Abiogenesis
Definition noun plural: abiogeneses a·bi·o·gen·e·sis, eɪbaɪəʊˈdʒɛnəsɪs (1) The idea that primitive life... Read More