Search Results for: physics
Biophysics
Physics as applied to biological problems.Merging the studies of physics into biology to assist greater knowledge in the... Read More
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Extraterrestrial
Definition adjective (astronomy) Of, pertaining to, relating to, or occurring beyond the earth's... Read More
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life
The FIFTH MIRACLE: The Search for the Origin and Meaning of Life ... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Physicology
physicology --> physics The science of nature, or of natural objects; that branch of science which treats of the laws and... Read More
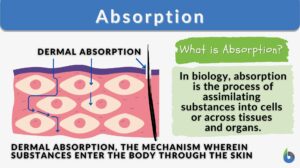
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More
Physical science
Definition noun Any of the sciences concerned with the study of non-living systems, such as the nature and properties of... Read More
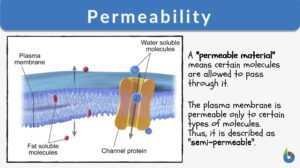
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More
Cross-sections
Cross-section (Science: physics) Usually refers to the (apparent) area presented by a target particle to an oncoming... Read More
Freezing point
Freezing point (Science: physics) The temperature at which a liquid solidifies. The temperature below which a liquid turns... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Photometers
photometer (Science: apparatus, physics) An instrument for measuring the intensity of light, or, more especially, for... Read More
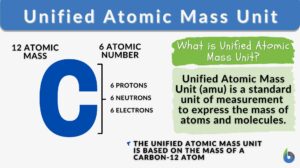
Atomic mass
Atomic mass (Science: chemistry, physics) The mass of an atom relative to other atoms. The present-day basis of the scale of... Read More
Biotechnology
Biotechnology Definition Biotechnology is a technology that uses biological systems or living organisms for a particular... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Branches of biology
What is a Branch of Biology? A branch of biology is a specialized field or a sub-discipline in a much broader field of... Read More
Neuroscience
Definition noun The branch of science that deals with the nervous system, particularly structure, development, function,... Read More
Light energy
Definition noun A form of energy consisting of particle-like photons with wavelike properties, and in which affects the... Read More
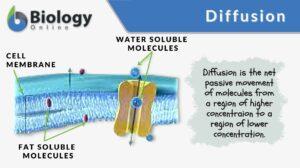
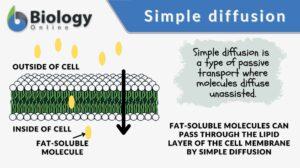
Simple diffusion
Diffusion is essential in the anatomy and physiology of a living thing, especially with regard to homeostasis. It is one of... Read More
Natural science
Definition noun The scientific study of phenomena or laws of the physical world. Supplement Natural science includes... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Electronegative
Electronegative (Science: chemistry, physics) Relating to or charged with negative electricity. Normally refers to an... Read More
Radioactive atom
Radioactive atom (Science: chemistry, physics) An atom with an unstable nucleus, which emits particulate or electromagnetic... Read More
Transducer
transducer (Science: physics) A device that transforms one type of energy to... Read More
Isodynamic
Isodynamic Of, pertaining to, having, or denoting, equality of force. (Science: physiology) isodynamic foods, those foods... Read More
Conduction
Conduction (Science: physics, physiology) The transfer of sound waves, heat, nervous impulses or electricity. Origin: L.... Read More


![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)