Search Results for: potentially
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
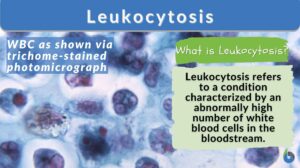
Leukocytosis
What Is Leukocytosis? Leukocytosis is a condition wherein the number of White Blood Cells (WBCs) is increased above the... Read More
Reproductive system
What is the Reproductive System? The reproductive system of an organism is the biological system made up of all the... Read More
Biological containment
Biological containment (Science: molecular biology) refers to any number of methods to contain genetically engineered... Read More
Thalassophobia
Among many psychological and psychiatric disorders, one is the fear of the ocean and the fear of deep water, which in... Read More
Chemotroph
Chemotroph Definition A chemotroph refers to an organism that obtains energy mainly from carbon dioxide and from... Read More
True breeding
Definition noun A kind of breeding in which the parents with a particular phenotype produce offspring only with the same... Read More
Thermophile
Thermophiles Definition What are thermophiles? Let us first understand the literal meaning of the word ‘thermophile’.... Read More
Medicinal plant
Definition noun Any plant whose roots, leaves, seeds, bark, or plant part is used for therapeutic, tonic, purgative, or... Read More
Demographic transition
The demographic transition model is a theoretical framework that explains the historical shift in population dynamics as a... Read More
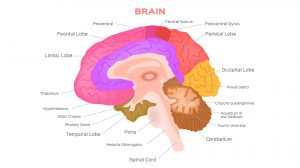
Human Neurology
Human Neurology deals essentially with the nervous system of humans. It also features the various theories put forward by... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
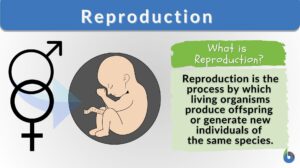
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
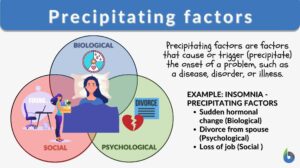
Precipitating factors
Precipitating Factor Definition Precipitating factors are factors that initiate or promote the onset of any illness,... Read More
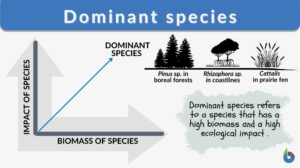
Dominant species
Dominance is the state of being supreme or dominant. Community dominance refers to the form of dominance where certain... Read More
Doderleins bacillus
Doderlein's bacillus is a large, Gram-positive bacterium found in vaginal secretions. It is named after the German... Read More
Inner cell mass
Inner cell mass a group of cells found in the mammalian blastocyst that give rise to the embryo and are potentially capable... Read More
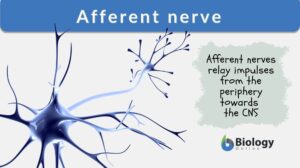
Afferent Nerve
Afferent Nerve Definition The word ‘aferent’ means "steering or conducting something towards a destination". The... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
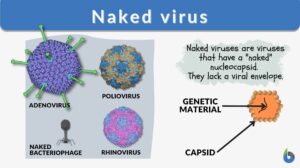
Naked virus
Viruses are infectious entities with size ranges between 20 to 400 nanometers. The mammoth-sized virus would be about the... Read More
Initial cell
Initial cell Actively dividing plant cell in a meristem. at each division one daughter cell remains in the meristem as a new... Read More
Agonal rhythm
Agonal Rhythm Definition Agonal rhythm is the slow, irregular heart rhythm (electrical activity of the heart), particularly... Read More