Search Results for: precise
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Origins of Life : On Earth and in the Cosmos (2nd Ed)
Origins of Life : On Earth and in the Cosmos ... Read More
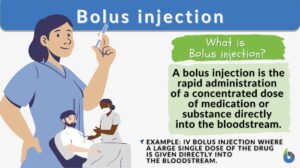
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
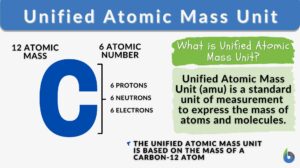
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Primitive Animals
Incorrect taxonomic classifications deemed organisms to be either animals or plants, in the Plantae or Animalia kingdoms... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Global Carbon Cycling on a Heterogeneous Seafloor
Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are the fundamental elements of life on Earth. Global carbon varies in amount and its... Read More
Primary structure
Definition noun (biochemistry) A structure of a biological molecule in which there is a precise sequence or order of... Read More
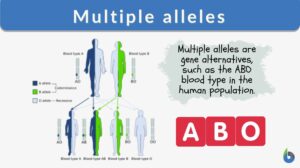
Multiple alleles
Alleles are the pairs of genes occupying a specific spot called locus on a chromosome. Typically, there are only two alleles... Read More
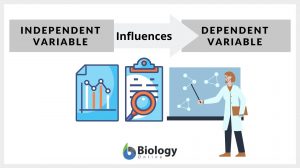
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Bacteriostat
Definition noun, plural: bacteriostats A biological or chemical agent causing bacteriostasis. Supplement Bacteriostatic... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Lights’ Effect on Growth
Plants are the primary producers of energy in any ecosystem, meaning that they bring in new energy to it which supports... Read More
Community (biology)
Community, in biology, refers to the assemblage of interacting organisms (either of the same or different species)... Read More
Shelfords Law of Tolerance
Definition noun It is a law stating that a certain organism’s survival and existence depend upon the multifaceted set of... Read More
Thistle tube
Definition noun A piece of glassware used in laboratory that consists of tube with funnel-like portion at the top and a... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Phagotrophy
Definition noun A process of ingesting relatively large particles of food that carries out via intracellular... Read More
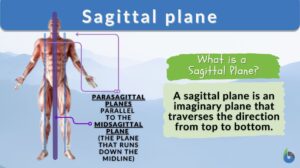
Sagittal plane
The sagittal plane is the plane that allows us to see the world in bilateral symmetry. Whether reaching for a high shelf,... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Amphimixis
Definition noun, plural: amphimixes The union or the fusion of the male and the female gametes during sexual... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More
Wobble hypothesis
wobble hypothesis (Science: molecular biology) explains why the base inosine is included in position 1 in the anticodons of... Read More
Woolly cheetah
Woolly cheetahs were reported in the 19th century as a separate species of cheetah that had longer, denser fur. Several... Read More
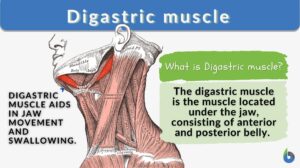
Digastric muscle
Digastric Definition The digastric muscle is a paired muscle located under the jaw, consisting of the anterior and... Read More
Subspecies
subspecies A group somewhat lessdistinct than speciesusually are, but based on characters more important than those which... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
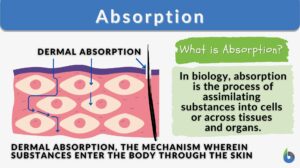
Absorption
Absorption can be defined as the process of assimilating substances across the intestinal epithelial cells or the tissues... Read More