Search Results for: pressure
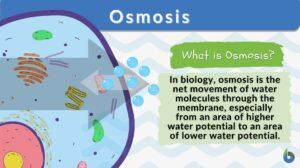
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
Blood pressure
Blood pressure (Science: cardiology, physiology) The force that the circulating blood exerts on the walls of the... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Air pressure
Definition noun (1) The pressure caused by the weight of air. (2) The force exerted by air per unit area. Supplement Air... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Hydrostatic pressure
Definition noun The pressure exerted or transmitted by the fluid (e.g. water) at rest. Supplement Hydrostatic pressure... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
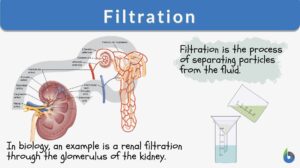
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
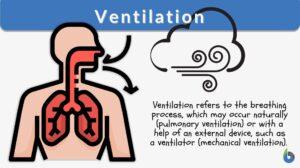
Ventilation
Ventilation Definition Often when persons think of ventilation, they think of getting clean or enough air into a room. This... Read More
Ventricular filling pressure
Definition noun The pressure that builds up in the ventricle as the ventricle is being filled with blood, typically... Read More
Partial pressure
partial pressure The pressure exerted by a single component of a mixture of gases, commonly expressed in mm hg or torr; for... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
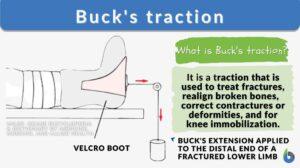
Buck’s traction
Buck's Traction Definition Buck's traction for femur fracture is very helpful. It can be utilized in the treatment and... Read More
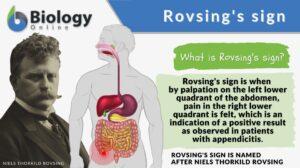
Rovsings sign
Rovsing's Sign Definition Rovsing's sign is when palpation on the left lower quadrant of the abdomen results in pain in the... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
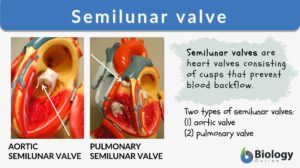
Semilunar valve
The human heart structure consists of heart chambers (2 atria and 2 ventricles) that differ functionally from each other.... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
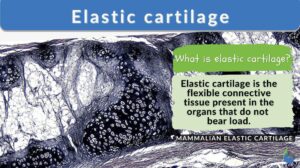
Elastic cartilage
The cartilage is a connective tissue characterized by having an extracellular matrix that is abundant in chondroitin sulfate... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)