Search Results for: proportional
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
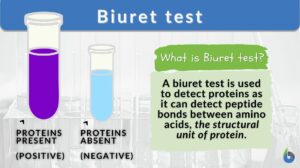
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More
Beer-Lambert law
Definition noun The principal law in spectrometry in which it states that the absorbance at a given wavelength of light is... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
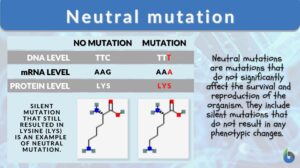
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
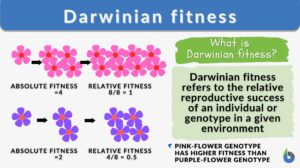
Darwinian fitness
Darwinian Fitness Definition Darwinian fitness refers to the measure of an individual organism's or genotype's reproductive... Read More
Graded potential
Definition noun, plural: graded potentials A change in the electrical potential on the membrane of an excitable cell (e.g. a... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Vant hoffs law
van't Hoff's law In stereochemistry, all optically active substances have one or more multivalent atoms united to four... Read More
Physical Development in Humans
The Newly Born Child Depending on the nutrients available to the child within pregnancy and the genetic makeup of the... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Kinetic molecular theory
Kinetic molecular theory (Science: chemistry) this theory assumes that molecules must collide in order to react. The more... Read More
Absorbance
Definition noun (analytical chemistry) A logarithmic measure of the amount of light absorbed (at particular wavelength) as... Read More
Chemokinesis
Definition noun A behavioral response of a cell or an organism to a soluble chemical that leads to random or directionally... Read More
Temperature
Temperature (Science: chemistry) temperature is proportional to the average random kinetic energy of ideal gases. The degree... Read More
Acromegaly
Acromegaly (Science: endocrinology) a condition that results from the excess production of growth hormone in the anterior... Read More
Valence electron
What are valence electrons? Why are they significant? Valence electrons definition in chemistry: The electrons in an atom's... Read More
Proportion
proportion 1. The relation or adaptation of one portion to another, or to the whole, as respect magnitude, quantity, or... Read More
Thermometer
thermometer (Science: physics) An instrument for measuring temperature, founded on the principle that changes of temperature... Read More
Electromagnetic radiation
Definition noun The radiation that consists of associated, interacting electric and magnetic field waves traveling at the... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Neuromelanin
Definition noun A type of melanin pigment present in parts of the brain, particularly in the neurons of substantia nigra and... Read More
Biotic potential
When we look at the different forms of life, we often wonder how they have continued to exist one generation after another.... Read More
Exponential growth
Definition noun A growth in which the rate is proportional to the increasing number or size in an exponential (rather than... Read More
Third-order kinetics
third-order kinetics (Science: pharmacology) A term describing the reaction rate of a chemical reaction in which the rate... Read More
Second-order kinetics
second-order kinetics A term describing the reaction rate of a chemical reaction in which the rate is proportional to the... Read More
Sensitivity and specificity
Definition noun Statistical measures for assessing the results of diagnostics and screening tests wherein sensitivity... Read More
Radial immunodiffusion
Definition noun A quantitative immunodiffusion technique used to detect the level of protein (antigen) in a sample by... Read More