Search Results for: ratio
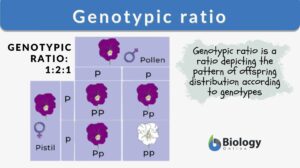
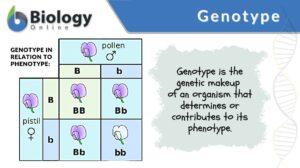
Genotypic ratio
Genotypic Ratio Definition To understand 'Genotypic ratio', let us first understand the terms: 'Genotype' and 'Phenotype'.... Read More
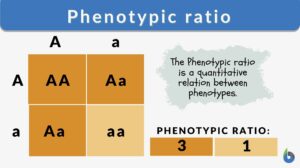
Phenotypic ratio
Phenotypic Ratio Definition How would one define phenotypic ratio? The correlation between the amount of offspring that... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Mass-action ratio
Mass-action ratio The ratio of the product of all of the product concentrations divided by the product of all of the... Read More
Molecular weight ratio
molecular weight ratio --> molecular weight The sum of the atomic weight's of all the atoms constituting a molecule; the... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio
nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio ratio of volume of nucleus to volume of cytoplasm, fairly constant for a particular cell type and... Read More
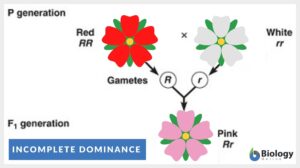
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete Dominance Definition After Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance laws, the term ''incomplete dominance'' was... Read More
Concentration
Definition noun (1) The measure of the amount of a sub-component (especially solute) in a solution (2) The ratio of the mass... Read More
SENI Biometric Analysis on the extinct Scincidae species: Macroscincus coctei (underlined)
Brian L. Schnirel Leeway Corucia Research Center (LCRC) Courtesy: Polyphemos (2004) Introduction: It has been... Read More
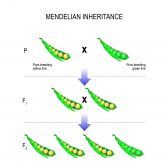
Inheritance and Probability
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is most famous in this field for his study... Read More
Proportion
proportion 1. The relation or adaptation of one portion to another, or to the whole, as respect magnitude, quantity, or... Read More
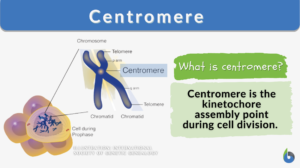
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
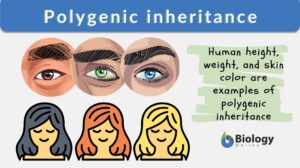
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Second filial generation
Definition noun (genetics) The filial generation comprised of offspring(s) resulting from a cross between two individuals... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
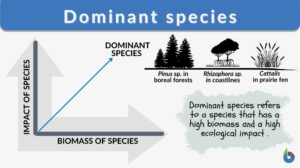
Dominant species
Dominance is the state of being supreme or dominant. Community dominance refers to the form of dominance where certain... Read More
Polygenic trait
Polygenic Trait Definition Polygenic trait refers to a trait that is controlled by multiple non-allelic genes. These genes... Read More
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. The inheritance patterns seen in Mendel's monohybrid and dihybrid crosses... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Erythrocyte
Erythrocyte Definition Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are the myeloid series of specialized cells that play an... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Biotic potential
When we look at the different forms of life, we often wonder how they have continued to exist one generation after another.... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Growth and Plant Hormones
Growth All living organisms begin in the same form: as a single cell. That cell will divide and the resulting cells will... Read More
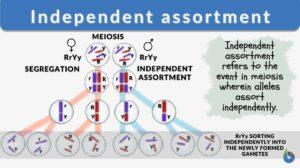
Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment Definition Independent assortment refers to the alleles or genes that sort into the newly formed... Read More
Test cross
Definition noun Crossing an organism with dominant genotype to a recessive homozygote for a specific phenotype in order to... Read More