Search Results for: require
Lights’ Effect on Growth
Plants are the primary producers of energy in any ecosystem, meaning that they bring in new energy to it which supports... Read More
Obligate aerobe
Before we define obligate aerobes, let us first understand and define aerobic organisms. Aerobic organisms are those that... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
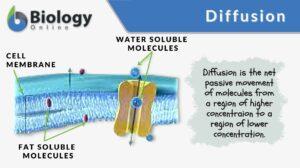
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
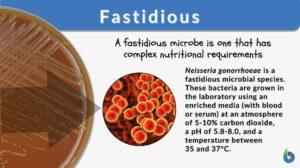
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
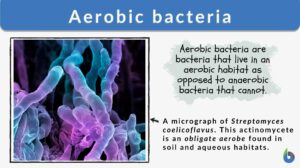
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
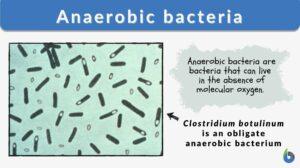
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
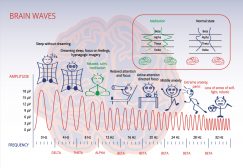
Sleep and Dreams – Neurology
The Falling Asleep Process During the day when we are awake, our body and brain are working tirelessly to operate our body,... Read More
Infradian rhythm
What is the Infradian Rhythm? An infradian rhythm is a type of biological rhythm that lasts longer than 24 hours, with a... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Dark reaction
Definition noun The series of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light to proceed, and ultimately... Read More
Flavoprotein
Definition noun, plural: flavoproteins A protein containing a flavin moiety, e.g. flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
Sex-linked trait
Definition of Sex-Linked Traits A sex-linked trait is an observable characteristic of an organism that is influenced by the... Read More
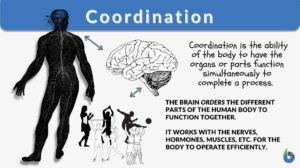
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Chronic disease
Chronic disease diseases which have one or more of the following characteristics: they are permanent, leave residual... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Saline solution
Saline Solution Definition Saline solution is one the most medically-used solution, which contains sodium chloride... Read More
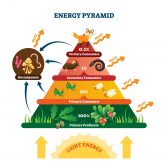
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
The previous tutorial on producers and consumers noted the reliance that organisms have on one another to obtain energy to... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More