Search Results for: residues
Nonapeptide
Definition noun, plural: nonapeptides An oligopeptide comprised of nine amino acid residues Supplement Peptides are monomers... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Contamination
Contamination Definition Contamination, sometimes interchanged with pollution, is the existence of live things or... Read More
Active site
Definition noun, plural: active sites The specific region of an enzyme where a substrate binds and catalysis takes place or... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Oligopeptide
Definition noun, plural: oligopeptides A peptide comprised of relatively small number of amino acid residues (i.e. about two... Read More
Signal sequence
Definition noun A sequence of amino acid residues bound at the amino terminus of a nascent protein during protein... Read More
Palmitic acid
Definition noun, plural: palmitic acids A 16-carbon fatty acid, with the formula: CH3 (CH2)14 COOH Supplement A fatty acid... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Alpha-helix
Definition noun, plural: alpha helices A right-handed coiled conformation common in many proteins in which the resulting... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Diacylglycerol
Diacylglycerol glycerol substituted on the 1 and 2 hydroxyl groups with long chain fatty acyl residues. Dag is a normal... Read More
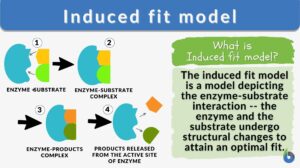
Induced fit model
Induced-Fit Model Definition The induced-fit model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction to depict the dynamic... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articles Frederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Millons test
Definition noun A color reaction test using Millon's reagent to detect phenolic compounds (e.g. tyrosine) Supplement French... Read More
Disulfide bond
Definition noun (chemistry) (1) The single covalent bond formed from the coupling of thiol groups, especially of cysteine... Read More
Elastic fiber
Definition noun, plural: elastic fibers A type of connective tissue fiber that is made up, primarily, of elastin, and found... Read More
Glycogenesis
Definition noun The metabolic process of producing glycogen from glucose for storage mainly in liver and muscle cells in... Read More
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Definition Noun A gram-positive facultative bacterium that produced slime for adhesions associated with endocarditis and... Read More
Mucolipidosis
Definition noun A type of mucopolysaccharides and mucolipids Supplement Lysosomal storage disease is a collective term for... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Brief Review on Climate Change and Tropical Peatlands
Peat soils are formed from biochemical process on moderately decomposed vegetation by aerobic microorganisms. It is mostly... Read More
A Protein Being Born – a live cell imaging of RNA translation
You probably already heard the concepts of translation in the central dogma of molecular biology. The dogma is an... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More