Search Results for: rnas
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
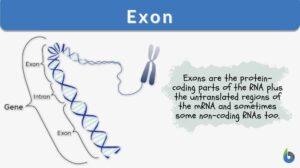
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Polynucleotide
Definition noun plural: polynucleotides pol·y·nu·cle·o·tide, ˌpɒlɪˈno͞o′klē-ə-tīd A biopolymer comprised of... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
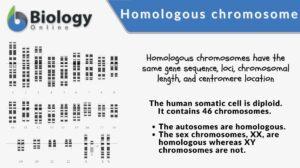
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Nuclear envelope
Definition noun plural: nuclear envelopes nu·cle·ar en·ve·lope, ˈn(j)ukliɚ ˈɛn.və.ləʊp The two layered membrane... Read More
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: ribosomal ribonucleic acids ri•bo•so•mal ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈraɪ... Read More
Wobble hypothesis
wobble hypothesis (Science: molecular biology) explains why the base inosine is included in position 1 in the anticodons of... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Prokaryotic Ancestor of Mitochondria: on the hunt
The alphaproteobacteria have been widely cited as the closest relative-- and possibly the prokaryotic ancestor -- of the... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA – hallmark of psychological stress
We often hear that stress can be unsettling as it could make us ill when it becomes chronic and overwhelming. However, is... Read More
Ribosomal DNA
Definition noun DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA Supplement Ribosomal DNA is the sequence of DNA that codes for... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA not just from moms but also from dads?
If one wants to trace down lineage, that person could turn to the cell's powerhouse, the mitochondrion. This organelle... Read More
Nuclear pore complex
Definition noun plural: nuclear pore complexes ˈnu kli ər, pɔː ˈkɒmplɛks A complex of nucleoporins resulting in the... Read More
Nucleoporin
Definition noun plural: nucleoporins Any of the family of porins that make up the nuclear pore complex Details Overview... Read More
Expression
Expression (Science: molecular biology) The process by which a genes coded information is converted into the structures... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
S1 nuclease mapping
Definition noun A laboratory method used to locate the 5'end of a transcript in a mixture of RNA using nuclease... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
Oligonucleotide
Definition noun plural: mononucleotides ol·i·go·nu·cle·o·tide, ŏl′ĭ-gō-no͞o′klē-ə-tīd A short polymer... Read More
Nuclear pore
Definition noun plural: nuclear pores ˈnu kli ər, pɔː Any of the many perforations on the nucleus as a result of the... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
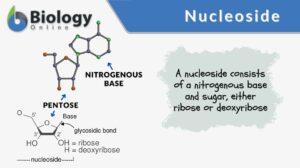
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Pribnow box
Pribnow box --> promoter (Science: molecular biology) A region of dNA to which rNA polymerase binds before initiating the... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More