Search Results for: sap
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Elaboration
Elaboration 1. The act or process of producing or refining with labour; improvement by successive operations; refinement. 2.... Read More
Karyolymph
Karyolymph The presumably fluid substance or gel of the nucleus in which stainable elements were believed to be suspended;... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Fauna
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we learned about the high biodiversity of New Zealand and how... Read More
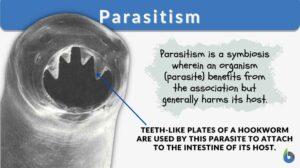
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Flora
By: Maria Victoria Gonzaga In the previous lesson, we've come to know some of the most fascinating endemic... Read More