Search Results for: schematic
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
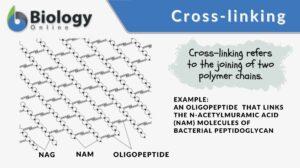
Cross-linking
Cross-linking Definition Cross-linking, in general, means the forming of cross-links between the joining structures. In... Read More
Phosphodiester bond
Phosphodiester Bond Definition Phosphodiester bonds are the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid present in the life... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Carrier protein
Carrier protein is a type of cell membrane protein involved in facilitated diffusion and active transport of substances out... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Micromolecule
Micromolecules Definition How to define micromolecule? Micromolecules are relatively small molecules that are combined... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
New Zealand’s Unique Geographical History
Written by: Maria Victoria Gonzaga Peer-reviewed by: Cathy Buntting, Ph.D. and Andrea Soanes New Zealand is... Read More
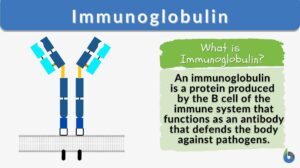
Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin Definition An immunoglobulin is a globulin molecule produced by the immune cells, for the body's defense... Read More
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
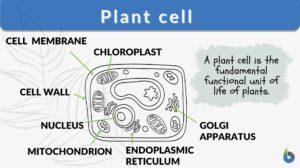
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
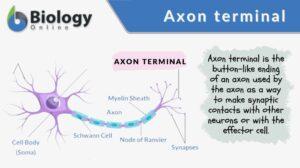
Axon terminal
An axon terminal is any of the button-like endings of axons through which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
Allopatric speciation
We can define speciation as a process by which the novel genetically independent group of organisms are formed through the... Read More
Turgor pressure
In biology, turgor pressure pertains to the pressure that is exerted by the fluid (e.g. water) against the cell wall. It is... Read More
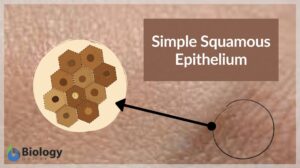
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Definition Simple squamous epithelium, also known as simple squamous epithelial tissue or... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Prokaryote
Prokaryote refers to any of the group of living organisms primarily characterized by the lack of a true nucleus and other... Read More
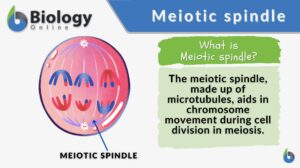
Meiotic spindle
Meiotic Spindle Definition The meiotic spindle refers to the spindle apparatus that forms during meiosis in contrast to... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Agonal rhythm
Agonal Rhythm Definition Agonal rhythm is the slow, irregular heart rhythm (electrical activity of the heart), particularly... Read More