Search Results for: serve
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Reservoir host
Reservoir Host Definition A reservoir host is a host that harbors the pathogen and serves as a source of the infective... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide Definition Biology Definition: A polysaccharide is a carbohydrate formed by long chains of repeating units... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Galacto-oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: galacto-oligosaccharides ga·lac·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride An oligosaccharide made up of... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Scleroprotein
Definition noun, plural: scleroproteins A type of protein characterized by being fibrous and its function which is to... Read More
Tight junction
What are tight junctions? Tight junctions are the intercellular barrier between two neighboring endothelial and epithelial... Read More
Spheroprotein
Definition noun, plural: spheroproteins A type of protein characterized by being globular or spherical in shape, and... Read More
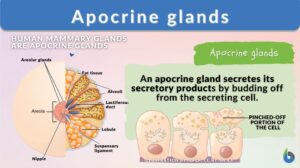
Apocrine gland
The human body is a complex assemblage of many different organs, systems, glands, bones, and tissues. Weighing any one over... Read More
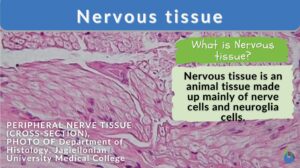
Nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue Definition Nerve cells (or neurons) and their associated cells, such as neuroglia cells, make up nervous... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
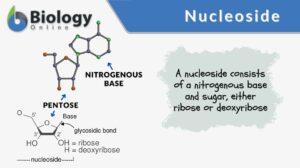
Nucleoside
Nucleoside Definition A nucleoside is a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine) bound to a pentose sugar ribose or... Read More
Diglyceride
Definition noun, plural: diglycerides A glyceride consisting of a glycerol and two fatty acid molecules joined through ester... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More