Search Results for: solvents
Fat solvents
Fat solvents organic liquids notable for their ability to dissolve lipids; usually, but not always, immiscible in water;... Read More
Polar solvents
polar solvents Solvent's that exhibit polar forces on solutes, due to high dipole moment, wide separation of charges, or... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Fat-soluble vitamin
Definition noun, plural: fat-soluble vitamins Any from the group of vitamins that are insoluble in water but soluble in fat... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic Definition The fear of mixing or reacting with water under a given set of reaction parameters is often referred... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
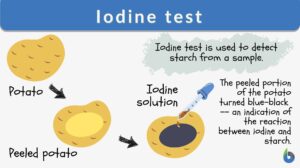
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
Methanotroph
Definition noun, plural: methanotrophs An organism that metabolize methane as a source of carbon and... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Water-soluble vitamin
Definition noun, plural: water-soluble vitamins Any of the group of vitamins that dissolve in water and excreted rather... Read More
Cell membrane permeability
Cell membrane permeability a quality of cell membranes which permits the passage of solvents and solutes into and out of... Read More
Indicators and reagents
Indicators and reagents substances used for the detection, identification, analysis, etc. Of chemical, biological, or... Read More
Volatile oil
Volatile Oil Definition Volatile oils are aromatic compounds that are characterized by their volatility and inability to... Read More
Solubility
Definition noun (1) The quantity of a particular substance (solid, liquid, or gas solute) that can dissolve in a particular... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More














![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)