Search Results for: stop
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
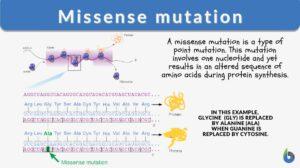
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Positive feedback
Positive Feedback Definition Each mechanism of the body like temperature, blood pressure, and levels of specific nutrients... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Environmental resistance
Environmental Resistance Definition Environmental resistance is such a process in which certain different elements or... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Osmotic pressure
Osmotic Pressure Definition Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by a difference in the amounts of solutes (or... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Haemostatic
Definition adjective (1) Capable of stopping haemorrhage or bleeding. (2) An agent or device that can arrest haemorrhage or... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Scientists brought dead pig brain partly back to life
Death is inevitable to any entity that has life. When there is a beginning there ought to be an end. However, the recent... Read More
Biological Cell Defense
Organisms must find a means of defense against antigens such a viruses described on the previous tutorial. If this was not... Read More
Carrying capacity
Carrying Capacity Definition What is carrying capacity? In biology and environmental science, the carrying capacity of a... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Consciousness and Behavior
States of Consciousness Defined either by (1) behavior - ranging from attentive and alert to coma and (2) electrical... Read More
Animal Growth Hormones
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. As mentioned in the previous tutorial, hormones are produced in... Read More
SELFISH GENE – selfish to persist
What is a selfish gene? A selfish gene is not a gene that makes an individual selfish. In fact, it may even be involved in... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulant An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents the clotting or thickening of blood. Anticoagulants are given to... Read More
Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis Definition Spermiogenesis is the stage of spermatogenesis wherein the spermatids differentiate into mature... Read More
Heterochrony
Definition noun, plural: heterochronies Refers to the rate of morphological transformations accomplish by the developmental... Read More
Pentapeptide
Definition noun, plural: pentapeptides A peptide containing five amino acids Supplement Peptides are biomolecules that are... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More










![Osmotic pressure n., plural: osmotic pressures [ɑsˈmɑtɪk ˈpɹɛʃ.ɚ] osmotic pressure definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/osmotic-pressure-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)